The structure of the educational program dow. It is advisable to highlight those features of the kindergarten educational process that distinguish it from other preschool educational institutions. Held annually in the school preparatory group


The structure and content of the educational program DOE
New approaches to management in the system of preschool education cause a change in the range of functions, principles, methods and techniques of managerial activity of heads of educational institutions. These changes are objective and are caused by the following main factors:

main factors:
formation of market relations, including in the social sphere, and, as a result, competition of educational institutions;
the establishment of an alternative system for escorting preschool children in the form of tutoring and private educational institutions;

main factors:
departure from a single program in the field of preschool education and the presence of a fan of curricula, manuals, didactic materials;
insufficient regulatory funding for preschool educational institutions;
opportunities to attract extrabudgetary funds to institutions;

main factors:
the interest of parents as the main social customers in the productive activities of a particular educational institution;
the desire of the public to influence the educational process in the institution, etc.

The optimal mechanism that provides these processes is the activity of a preschool educational institution in the development and implementation of its basic general education program (OOP)

The basic general educational program (OOP) is a mandatory regulatory document developed and implemented, according to paragraph 5, Art. 14 of the Law of the Russian Federation “On Education”, “by each educational institution independently”

Order of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation of November 23, 2009 N 655 "On approval and enforcement of federal state requirements for the structure of the basic general educational program of preschool education"

The PLO of a preschool educational institution is one of the main regulatory documents governing its life.
It, along with the Charter, serves as the basis for accreditation, changes in budget financing, and the organization of paid educational services in accordance with the social order of parents (legal representatives).

The main educational program of a preschool educational institution is
regulatory document justifying the choice goals content applied methods and technologies, forms organization of the educational process in each specificpreschool educational institution

OOP DOU is considered as a model for organizing the educational process focused on the personality of the pupil and taking into account the type of preschool educational institution, as well as priority areas of activity

PLO and Charter
The charter is a legal document, a kind of constitution of an educational institution. It determines the features of the functioning of the entire educational institution as a whole.
OOP determines the content of the educational process, detailing the standardization of its components

OOP and educational standards
Temporary standards for preschool education determine the compulsory part of preschool education and the requirements for the level of assimilation of this content.
The means of implementing the standard is a combination of basic and partial programs developed individually by each educational institution and recorded in the PLO

OOP and development program
PLO is aimed at realizing the goals of raising, developing and educating children, that is, at the successful implementation and development of the directly pedagogical component of the educational institution
A development program is a type of targeted program. Unlike OOP, she optional normative document for an educational institution and is primarily aimed at solving the most actual issues the entire educational institution as a whole, while affecting all aspects of its life: economic, regulatory, material and technical, etc.

PLO and the concept of an educational institution
A concept is an integral, necessary part of a development program. It is a system of values \u200b\u200band norms that the teaching staff of an educational institution chooses for itself and which it intends to use in its professional activities.
OOP acts in this case as a complex condition for the implementation of the concept.

OOP and experimental work program
OOP in this case is one of the options for organizing the experimental work
If the DOE is an experimental site of any level, then together with the supervisor it develops an experimental program that includes the substantiation of the problem, the hypothesis of the study, the definition of the object and subject of work, a theoretical analysis of the basic concepts, as well as the methodological part. It is aimed at determining the effectiveness of certain innovations.

PLO and state accreditation procedures
In this case, the educational program of the pre-school educational institution is the basis and basis for the high-quality and successful passage of the indicated procedure.
If, as a result of planned development, an educational institution wants to change its status, then on the basis of a developed and implemented general educational program, in which the sought status (type and type) should already be indicated, it, in accordance with the approved procedure, undergoes the state procedure accreditation and subsequently, by its results, it receives one or another status.

Thus, the process of development and implementation of educational programs can be considered as a process of harmonization of state educational standards, social order for a particular educational institution and its pedagogical capabilities


Clause 4, Article 7 of the Federal Law "On Education"
Under “The structure of basic educational programs” the ratio and volume of their parts is understood, as well as the ratio of the compulsory part of the main educational program and the part formed by the participants in the educational process.

Recommended structure of the PLO of a preschool educational institution
Mandatory part Programs
The second part (variable)Programs formed by participants in the educational process
Applications to the program.

Analysis of existing (comprehensive) programs
Kindergarten education and training program/ Ed. M.A. Vasilyeva, V.V. Herbovoi, T.S. Komarova (2005 version).
Rainbow: Program for the upbringing, education and development of preschool children in kindergarten / T.N. Doronova, S.G. Jacobson, E.V. Soloviev and others; Scientific hands. T.N. Doronova.
Childhood: Program for the development and education of children in kindergarten / V.I. Loginova, T.I. Babaeva, N.A. Notkina et al .; Ed. T.I. Babaeva, Z.A. Mikhailova, L.M. Gurovich,
Sample general educational program for the education, training and development of children of early and preschool age / Ed. L.A. Paramonova.

conclusions
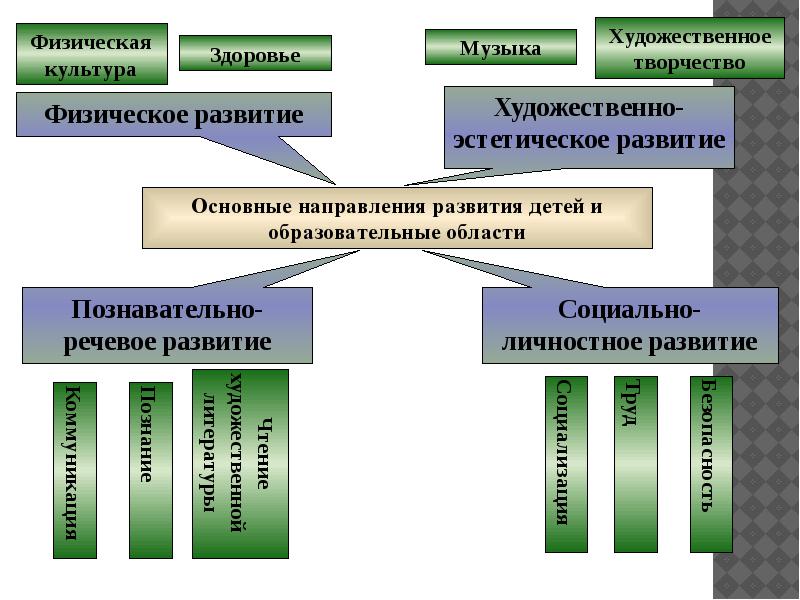
1) “cementing” basis for the content of preschool education in the conditions of its variability are 4 areas that correspond to the main lines of development of the child: - cognitive and speech;
- physical;
- social and personal;
- artistic and aesthetic.

conclusions

Recommended structure of the PLO of a preschool educational institution
Mandatory part Programs
The second part (variable)Programs formed by participants in the educational process
Applications to the program.

Analysis of existing (comprehensive) programs
Kindergarten education and training program/ Ed. M.A. Vasilyeva, V.V. Herbovoi, T.S. Komarova (2005 version).
Rainbow: Program for the upbringing, education and development of preschool children in kindergarten / T.N. Doronova, S.G. Jacobson, E.V. Soloviev and others; Scientific hands. T.N. Doronova.
Childhood: Program for the development and education of children in kindergarten / V.I. Loginova, T.I. Babaeva, N.A. Notkina et al .; Ed. T.I. Babaeva, Z.A. Mikhailova, L.M. Gurovich,
Sample general educational program for the education, training and development of children of early and preschool age / Ed. L.A. Paramonova.

conclusions
1) “cementing” basis for the content of preschool education in the conditions of its variability are 4 areas that correspond to the main lines of development of the child: - cognitive and speech;
- physical;
- social and personal;
- artistic and aesthetic.

conclusions
Kindergarten education and training program/ Ed. M.A. Vasilyeva, V.V. Herbovoi, T.S. Komarova (2005 version).
Rainbow: Program for the upbringing, education and development of preschool children in kindergarten / T.N. Doronova, S.G. Jacobson, E.V. Soloviev and others; Scientific hands. T.N. Doronova.
Childhood: Program for the development and education of children in kindergarten / V.I. Loginova, T.I. Babaeva, N.A. Notkina et al .; Ed. T.I. Babaeva, Z.A. Mikhailova, L.M. Gurovich,
Sample general educational program for the education, training and development of children of early and preschool age / Ed. L.A. Paramonova.
- cognitive and speech;
- physical;
- social and personal;
- artistic and aesthetic.

conclusions
2) the "fullness" of each of the above areas in the analyzed programs is heterogeneous in quantitative and qualitative terms;
3) there is currently no single point of view on what the content should be preschool educationto ensure graduate achievement kindergarten the level of physical and psychological readiness for school for the successful development of the basic general educational programs of primary general education; 
4) the amount of educational load in the main areas of development of children in existing programs is distributed quite unequally: 1st place - cognitive-speech development (from 40 to 47% of classes);
2nd place - artistic and aesthetic development (from 20 to 40%);
3rd place - physical development (19-20%).
4th place - social and personal development (from 0 to 13%).

conclusions
1st place - cognitive-speech development (from 40 to 47% of classes);
2nd place - artistic and aesthetic development (from 20 to 40%);
3rd place - physical development (19-20%).
4th place - social and personal development (from 0 to 13%).
5) in the framework of the above main areas (social, personal, physical, cognitive and speech, artistic and aesthetic), the amount of educational load on various types of activities of children (playing, speech, productive, etc.) is also presented unequally, in violation of the principles of age approach to children's education preschool age and SanPiN requirements. 
“Integration of the content of preschool education” –
the state (or the process leading to such a state) of the connectedness, interpenetration and interaction of individual educational areas of preschool education, ensuring the integrity of the educational process.

Recommendations for developing the content of OOP sections

“A compulsory part of the basic general educational program of preschool education”–
the state (or the process leading to such a state) of the connectedness, interpenetration and interaction of individual educational areas of preschool education, ensuring the integrity of the educational process.

Recommendations for developing the content of OOP sections

“A compulsory part of the basic general educational program of preschool education”–

Recommendations for developing the content of OOP sections

“A compulsory part of the basic general educational program of preschool education”–
part of the main general education program, which should be implemented in any educational institution (group) that implements the basic general educational program of preschool education. Ensures the achievement of pupils readiness for school.In compensating and combined focus includes activities for the qualified correction of deficiencies in the physical and (or) mental development children with disabilities health.

explanatory note;
organization of the stay of children in an educational institution;
the content of psychological and pedagogical work on the development of physical education by children “Physical Culture”, “Health”, “Safety”, “Socialization,“ Labor ”,“ Cognition ”,“ Communication ”,“ Reading fiction ”,“ Artistic creation ”,“ Music";

The mandatory part of the Program should contain the following sections:
the content of correctional work (for children with disabilities);
the planned results of mastering by children the basic general educational program of preschool education;
a monitoring system for children's achievement of the planned results of the Program.

The second part of the program, formed by the participants of the educational process, should reflect:
1) the species diversity of institutions,
the availability of priority areas of activity, including the provision of equal starting opportunities for the education of children in educational institutions,
“Part of the basic general educational program of preschool education, formed by participants in the educational process” –
it is part of the basic pre-school educational program formed by the participants educational process in addition to the mandatory part, and reflecting: 1) the species diversity of institutions (groups), the presence of priority areas of activity (except for the activities of qualified correction of deficiencies in the physical and (or) mental development of children with disabilities); 2) the specifics of socio-economic, national-cultural, demographic, climatic and other conditions in which the educational process is carried out.

Each preschool educational institution has its own individual, unique to it means of fulfilling its mission.
It is them that must be designated.

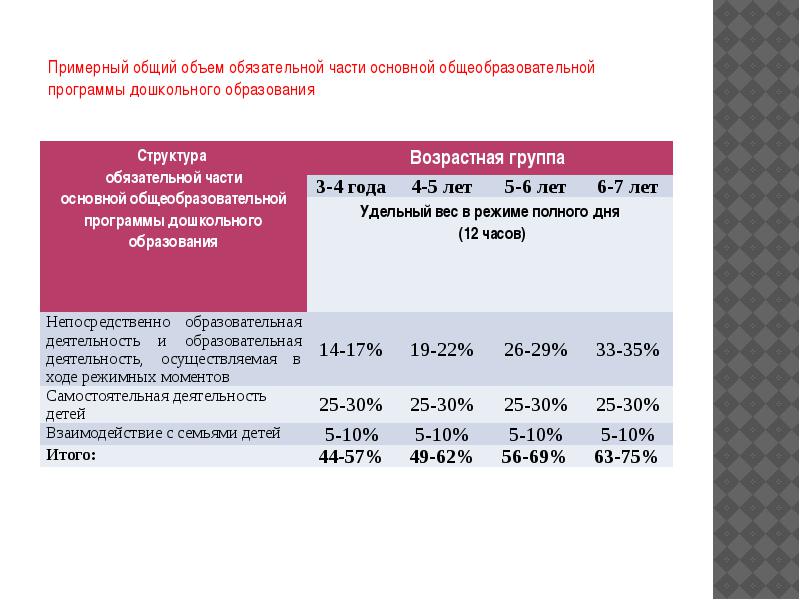
The total amount of the compulsory part of the main general educational program, which should be implemented in any educational institution (group), except for compensating and combined groups,
calculated in accordance with the age of the pupils, the main directions of their development, the specifics of preschool education and includes the time allotted for: directly educational activities;
educational activities carried out during sensitive moments;
interaction with families of children on the implementation of the basic general educational program of preschool education

The approximate total amount of the compulsory part of the basic general educational program of preschool education
The amount of the mandatory part of the basic general educational program of preschool education does not include the time allotted for: joint activities of adults and children, carried out during regimen moments and aimed at the implementation of the functions of supervision and (or) care;
daytime sleep (in groups of full, shortened, extended day and round-the-clock stay).

directly educational activities;
educational activities carried out during sensitive moments;
interaction with families of children on the implementation of the basic general educational program of preschool education
joint activities of adults and children, carried out during regimen moments and aimed at the implementation of the functions of supervision and (or) care;
daytime sleep (in groups of full, shortened, extended day and round-the-clock stay).
The optimal is the equal-share ratio of the volumes of the compulsory part of the basic general educational program of pre-school education in the main areas of children's development, such as physical, social, personal, cognitive and speech, artistic and aesthetic (approximately 25% of the total volume). 
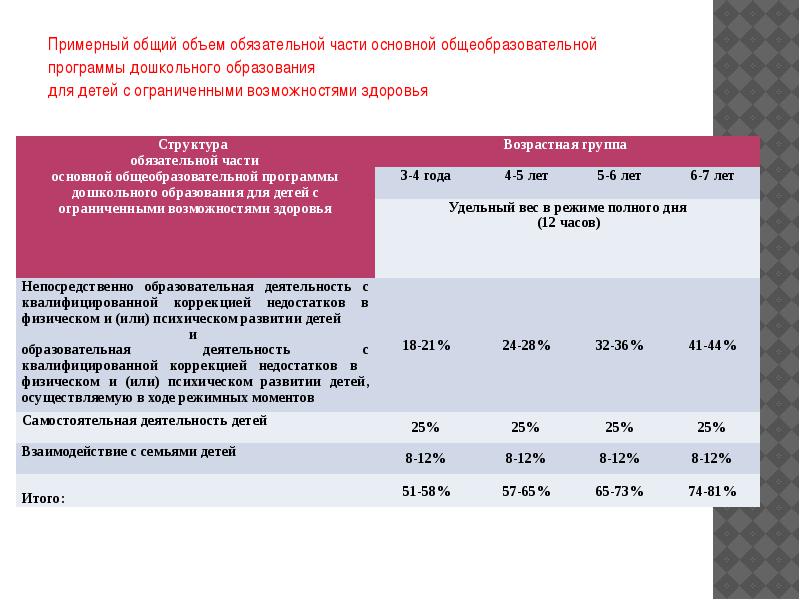
The total amount of the compulsory part of the main educational program for children with disabilities, which should be implemented in compensating and combined groups,
includes time allotted for: directly educational activities with qualified correction of deficiencies in the physical and (or) mental development of children;
educational activities with qualified correction of deficiencies in the physical and (or) mental development of children, carried out during regime moments;
independent activity of children;
interaction with families of children on the implementation of the basic general education program for preschool education for children with disabilities

The approximate total amount of the compulsory part of the basic general education program for preschool education for children with disabilities
an additional 5-6% to the directly educational activities of children and educational activities carried out during regime moments, an obligatory part of the main general educational program, if the institution, according to the results of state accreditation, has one priority area of \u200b\u200bactivity;
an additional 11-12%, if the institution according to the results of state accreditation has two priority areas of activity;

The approximate total volume of the part formed by the participants in the educational process
an additional 17-18%, if the institution according to the results of state accreditation has three priority areas of activity;
an additional 24-25% if the institution, according to the results of state accreditation, has all areas of activity priority.

“Joint activities of adults and children” -
directly educational activities with qualified correction of deficiencies in the physical and (or) mental development of children;
educational activities with qualified correction of deficiencies in the physical and (or) mental development of children, carried out during regime moments;
independent activity of children;
interaction with families of children on the implementation of the basic general education program for preschool education for children with disabilities
an additional 5-6% to the directly educational activities of children and educational activities carried out during regime moments, an obligatory part of the main general educational program, if the institution, according to the results of state accreditation, has one priority area of \u200b\u200bactivity;
an additional 11-12%, if the institution according to the results of state accreditation has two priority areas of activity;

The approximate total volume of the part formed by the participants in the educational process
an additional 17-18%, if the institution according to the results of state accreditation has three priority areas of activity;
an additional 24-25% if the institution, according to the results of state accreditation, has all areas of activity priority.

“Joint activities of adults and children” -
an additional 17-18%, if the institution according to the results of state accreditation has three priority areas of activity;
an additional 24-25% if the institution, according to the results of state accreditation, has all areas of activity priority.

“Joint activities of adults and children” -
the activity of two or more participants in the educational process (adults and pupils) in solving educational problems in one space and at the same time. It is distinguished by the presence of a partner (equal) position of an adult and a partner form of organization (the possibility of free placement, movement and communication of children in the process educational activities) It involves individual, subgroup and group forms of organization of work with pupils. 
"Independent activity of children" -
1) the free activities of the pupils in the conditions created by the teachers of the subject-developing educational environment, ensuring that each child chooses an activity of interest and allows him to interact with peers or act individually;
2) the activities of the pupils organized by the teacher aimed at solving problems related to the interests of other people (emotional well-being of other people, helping others at home, etc.).

Basic pre-school educational program
should: To ensure the protection and strengthening of children's health, their comprehensive (physical, cognitive-speech, artistic-aesthetic, social and personal) development through the organization of various types of children's activities and amateur activities, the leading of which is the game.

To help the child achieve a level of development that ensures his psychological and physical readiness for school, create equal conditions for the upbringing, development and training of children, regardless of the material wealth of the family, place of residence, linguistic and cultural environment, ethnicity.
Comply with the principle of developing education, the purpose of which is the development of the child.

To meet the criteria of completeness, necessity and sufficiency (to allow solving the set goals and objectives only on the necessary and sufficient material, as close as possible to a reasonable "minimum").
To form such qualities, knowledge, skills that are directly related to the development of preschool children.

Based on a comprehensive thematic principle of building the educational process. Program topics should be accessible to children and evoke a positive emotional attitude, necessary for them to develop appropriate motivation in the educational process.
It is based on age-appropriate forms of working with children in the form of games, conversations, reading, observations, etc. The main form of working with preschool children is a game that is set in the educational process by adults.

Explanatory note

The purpose and objectives of the educational process
Purpose:
- Creation of an integrated system for the physical education and health of children. Tasks:
To ensure the protection and strengthening of children's health, their comprehensive (physical, cognitive-speech, artistic-aesthetic, social and personal) development through the organization of various types of children's activities and amateur activities, the leading of which is the game.

To help the child achieve a level of development that ensures his psychological and physical readiness for school, create equal conditions for the upbringing, development and training of children, regardless of the material wealth of the family, place of residence, linguistic and cultural environment, ethnicity.
Comply with the principle of developing education, the purpose of which is the development of the child.

To meet the criteria of completeness, necessity and sufficiency (to allow solving the set goals and objectives only on the necessary and sufficient material, as close as possible to a reasonable "minimum").
To form such qualities, knowledge, skills that are directly related to the development of preschool children.

Based on a comprehensive thematic principle of building the educational process. Program topics should be accessible to children and evoke a positive emotional attitude, necessary for them to develop appropriate motivation in the educational process.
It is based on age-appropriate forms of working with children in the form of games, conversations, reading, observations, etc. The main form of working with preschool children is a game that is set in the educational process by adults.

Explanatory note

The purpose and objectives of the educational process
Purpose:
- Creation of an integrated system for the physical education and health of children. Tasks:
To ensure the protection and strengthening of children's health, their comprehensive (physical, cognitive-speech, artistic-aesthetic, social and personal) development through the organization of various types of children's activities and amateur activities, the leading of which is the game.

To help the child achieve a level of development that ensures his psychological and physical readiness for school, create equal conditions for the upbringing, development and training of children, regardless of the material wealth of the family, place of residence, linguistic and cultural environment, ethnicity.
Comply with the principle of developing education, the purpose of which is the development of the child.

To meet the criteria of completeness, necessity and sufficiency (to allow solving the set goals and objectives only on the necessary and sufficient material, as close as possible to a reasonable "minimum").
To form such qualities, knowledge, skills that are directly related to the development of preschool children.

Based on a comprehensive thematic principle of building the educational process. Program topics should be accessible to children and evoke a positive emotional attitude, necessary for them to develop appropriate motivation in the educational process.
It is based on age-appropriate forms of working with children in the form of games, conversations, reading, observations, etc. The main form of working with preschool children is a game that is set in the educational process by adults.

Explanatory note

The purpose and objectives of the educational process
Purpose:
- Creation of an integrated system for the physical education and health of children. Tasks:

To meet the criteria of completeness, necessity and sufficiency (to allow solving the set goals and objectives only on the necessary and sufficient material, as close as possible to a reasonable "minimum").
To form such qualities, knowledge, skills that are directly related to the development of preschool children.

Based on a comprehensive thematic principle of building the educational process. Program topics should be accessible to children and evoke a positive emotional attitude, necessary for them to develop appropriate motivation in the educational process.
It is based on age-appropriate forms of working with children in the form of games, conversations, reading, observations, etc. The main form of working with preschool children is a game that is set in the educational process by adults.

Explanatory note

The purpose and objectives of the educational process
Purpose:
- Creation of an integrated system for the physical education and health of children. Tasks:

The purpose and objectives of the educational process
Purpose:
- Creation of an integrated system for the physical education and health of children. Tasks:
Tasks:
To ensure the rational organization of motor activity of children; - create conditions for wellness regimes of children; - strengthen attention to the formation of proper posture; - contribute to the formation of a healthy lifestyle in children in constant interaction with the family. 
1. A comprehensive program of preschool education "Rainbow"(bibliographic description of the document in accordance with GOST).
2. Partial programs:
- “Our home is nature” (N. Ryzhova); - “Start” (L. Yakovleva, R. Rodina) and others. Partial programs should be selected in order to “strengthen” any least developed sections of the complex program.

3. The correction program for special (correctional) educational institutions of the 4th type (for children with visual impairment), ed. L.I. Plaksina.

4. Scientific and methodological materials substantiating the content of correctional work in kindergarten, for example:
- A.V. Grishvina, E.Ya. Puzyrevskaya, E.V. Sochevanova. "Game-classes with young children with impaired mental and speech development"; - N.D. Shmatko. "Children with developmental disabilities", etc.

1. Organization of the mode of stay of children in an educational institution

A flexible mode of activity depending on the social order of parents, the availability of specialists, teachers, medical workers, approaches to the development and education of preschool children, to the organization of all types of children's activities

Schedules of interaction between teachers, specialists and educators;
A model of the educational process using various forms and taking into account the time of year and age-related psychophysiological capabilities of children, the relationship of planned activities with the daily life of children in kindergarten

- A system of hardening measures;
- A system of fitness activities

2. The content of psychological and pedagogical work on the development of educational areas by children

3. The content of correctional work (for children with disabilities

includes activities to correct deficiencies in the physical and (or) mental development of children with disabilities.
This section also includes a selection of programs and technologies used in preschool education in accordance with the direction of correction

4. Planned results for children to master the basic general education program of preschool education

Midterm assessment
(once every six months or once a year) - this is a description of the dynamics of the formation of the integrative qualities of pupils of each age group for their development of the Program in all areas of children's development;
are monitoring results

final grade
it is carried out when a child is released from kindergarten to school and includes a description of the integrative qualities of a graduate of a preschool educational institution.
Held annually in the preparatory group for the school.
A portrait of a graduate can be drawn up by the teaching staff of the preschool educational institution, taking into account regulatory documents

5. A system for monitoring the achievement by children of the planned results of mastering the Program

Child achievement monitoring system the planned results of the development of the Program should provide an integrated assessment approach final and intermediate Program development results, allow assessing the dynamics of children's achievements and include description of the object, forms, frequency and contentmonitoring.

The monitoring process examines the physical, intellectual and personal qualities

Planned time for a psychological and pedagogical diagnosis of the results of the development of the Program: 5-7 days in September and May.


Features of the organization of the educational process
The section describes the features of the organization of the educational process in the preschool educational institution, which ensure the achievement of the planned results of joint activities, for example:

In the mode of operation of a preschool educational institution; - in leading forms of conducting classes; - in the organization of the subject-development environment; - in the selection of personnel; - in the features of the organization and conduct of various events; - in the establishment of social partnership; - in interaction with the family; - in the traditions of a preschool educational institution, etc.

It is advisable to highlight those features of the kindergarten educational process that distinguish it from other preschool educational institutions.
For example, the organization of the work of groups separately for boys and girls; short stay, etc.

It is also recommended to note the additional educational services provided by the institution both within the framework of budgetary financing and on a paid basis, which reinforce the priority line of activity chosen by the kindergarten.

OOP Applications
- the composition of the working group on the development of EP; - work plan of the working group; - expert opinion on the OP; - Protocol of the pedagogical council on the approval of the OP; - an order on a preschool educational institution on the implementation of EPs indicating those responsible for certain areas; - plan for the implementation of the educational program of the DOE; - diagnostic techniques (“tool”) to section 6;

OOP Applications
Glossary of basic terms used by members of the teaching staff within the educational institution; - the results of diagnostics of the implementation of the educational program; - analytical materials substantiating the content of sections of the educational program; - analytical materials justifying the need for changes and additions to sections of the educational program.

Kornilova Marina Vladimirovna,

3. The correction program for special (correctional) educational institutions of the 4th type (for children with visual impairment), ed. L.I. Plaksina.

4. Scientific and methodological materials substantiating the content of correctional work in kindergarten, for example:
- A.V. Grishvina, E.Ya. Puzyrevskaya, E.V. Sochevanova. "Game-classes with young children with impaired mental and speech development"; - N.D. Shmatko. "Children with developmental disabilities", etc.

1. Organization of the mode of stay of children in an educational institution

A flexible mode of activity depending on the social order of parents, the availability of specialists, teachers, medical workers, approaches to the development and education of preschool children, to the organization of all types of children's activities

Schedules of interaction between teachers, specialists and educators;
A model of the educational process using various forms and taking into account the time of year and age-related psychophysiological capabilities of children, the relationship of planned activities with the daily life of children in kindergarten

- A system of hardening measures;
- A system of fitness activities

2. The content of psychological and pedagogical work on the development of educational areas by children


3. The content of correctional work (for children with disabilities

includes activities to correct deficiencies in the physical and (or) mental development of children with disabilities.
This section also includes a selection of programs and technologies used in preschool education in accordance with the direction of correction

4. Planned results for children to master the basic general education program of preschool education

Midterm assessment
(once every six months or once a year) - this is a description of the dynamics of the formation of the integrative qualities of pupils of each age group for their development of the Program in all areas of children's development;
are monitoring results

final grade
it is carried out when a child is released from kindergarten to school and includes a description of the integrative qualities of a graduate of a preschool educational institution.
Held annually in the preparatory group for the school.
A portrait of a graduate can be drawn up by the teaching staff of the preschool educational institution, taking into account regulatory documents

5. A system for monitoring the achievement by children of the planned results of mastering the Program

Child achievement monitoring system the planned results of the development of the Program should provide an integrated assessment approach final and intermediate Program development results, allow assessing the dynamics of children's achievements and include description of the object, forms, frequency and contentmonitoring.

The monitoring process examines the physical, intellectual and personal qualities

Planned time for a psychological and pedagogical diagnosis of the results of the development of the Program: 5-7 days in September and May.


Features of the organization of the educational process
The section describes the features of the organization of the educational process in the preschool educational institution, which ensure the achievement of the planned results of joint activities, for example:

In the mode of operation of a preschool educational institution; - in leading forms of conducting classes; - in the organization of the subject-development environment; - in the selection of personnel; - in the features of the organization and conduct of various events; - in the establishment of social partnership; - in interaction with the family; - in the traditions of a preschool educational institution, etc.

It is advisable to highlight those features of the kindergarten educational process that distinguish it from other preschool educational institutions.
For example, the organization of the work of groups separately for boys and girls; short stay, etc.

It is also recommended to note the additional educational services provided by the institution both within the framework of budgetary financing and on a paid basis, which reinforce the priority line of activity chosen by the kindergarten.


OOP Applications
- the composition of the working group on the development of EP; - work plan of the working group; - expert opinion on the OP; - Protocol of the pedagogical council on the approval of the OP; - an order on a preschool educational institution on the implementation of EPs indicating those responsible for certain areas; - plan for the implementation of the educational program of the DOE; - diagnostic techniques (“tool”) to section 6;

OOP Applications
Glossary of basic terms used by members of the teaching staff within the educational institution; - the results of diagnostics of the implementation of the educational program; - analytical materials substantiating the content of sections of the educational program; - analytical materials justifying the need for changes and additions to sections of the educational program.

Kornilova Marina Vladimirovna,

A flexible mode of activity depending on the social order of parents, the availability of specialists, teachers, medical workers, approaches to the development and education of preschool children, to the organization of all types of children's activities

Schedules of interaction between teachers, specialists and educators;
A model of the educational process using various forms and taking into account the time of year and age-related psychophysiological capabilities of children, the relationship of planned activities with the daily life of children in kindergarten

- A system of hardening measures;
- A system of fitness activities

2. The content of psychological and pedagogical work on the development of educational areas by children


3. The content of correctional work (for children with disabilities

includes activities to correct deficiencies in the physical and (or) mental development of children with disabilities.
This section also includes a selection of programs and technologies used in preschool education in accordance with the direction of correction

4. Planned results for children to master the basic general education program of preschool education

Midterm assessment
(once every six months or once a year) - this is a description of the dynamics of the formation of the integrative qualities of pupils of each age group for their development of the Program in all areas of children's development;
are monitoring results

final grade
it is carried out when a child is released from kindergarten to school and includes a description of the integrative qualities of a graduate of a preschool educational institution.
Held annually in the preparatory group for the school.
A portrait of a graduate can be drawn up by the teaching staff of the preschool educational institution, taking into account regulatory documents

5. A system for monitoring the achievement by children of the planned results of mastering the Program

Child achievement monitoring system the planned results of the development of the Program should provide an integrated assessment approach final and intermediate Program development results, allow assessing the dynamics of children's achievements and include description of the object, forms, frequency and contentmonitoring.

The monitoring process examines the physical, intellectual and personal qualities

Planned time for a psychological and pedagogical diagnosis of the results of the development of the Program: 5-7 days in September and May.


Features of the organization of the educational process
The section describes the features of the organization of the educational process in the preschool educational institution, which ensure the achievement of the planned results of joint activities, for example:

In the mode of operation of a preschool educational institution; - in leading forms of conducting classes; - in the organization of the subject-development environment; - in the selection of personnel; - in the features of the organization and conduct of various events; - in the establishment of social partnership; - in interaction with the family; - in the traditions of a preschool educational institution, etc.

It is advisable to highlight those features of the kindergarten educational process that distinguish it from other preschool educational institutions.
For example, the organization of the work of groups separately for boys and girls; short stay, etc.

It is also recommended to note the additional educational services provided by the institution both within the framework of budgetary financing and on a paid basis, which reinforce the priority line of activity chosen by the kindergarten.


OOP Applications
- the composition of the working group on the development of EP; - work plan of the working group; - expert opinion on the OP; - Protocol of the pedagogical council on the approval of the OP; - an order on a preschool educational institution on the implementation of EPs indicating those responsible for certain areas; - plan for the implementation of the educational program of the DOE; - diagnostic techniques (“tool”) to section 6;

OOP Applications
Glossary of basic terms used by members of the teaching staff within the educational institution; - the results of diagnostics of the implementation of the educational program; - analytical materials substantiating the content of sections of the educational program; - analytical materials justifying the need for changes and additions to sections of the educational program.

Kornilova Marina Vladimirovna,

includes activities to correct deficiencies in the physical and (or) mental development of children with disabilities.
This section also includes a selection of programs and technologies used in preschool education in accordance with the direction of correction

4. Planned results for children to master the basic general education program of preschool education

Midterm assessment
(once every six months or once a year) - this is a description of the dynamics of the formation of the integrative qualities of pupils of each age group for their development of the Program in all areas of children's development;
are monitoring results

final grade
it is carried out when a child is released from kindergarten to school and includes a description of the integrative qualities of a graduate of a preschool educational institution.
Held annually in the preparatory group for the school.
A portrait of a graduate can be drawn up by the teaching staff of the preschool educational institution, taking into account regulatory documents

5. A system for monitoring the achievement by children of the planned results of mastering the Program

Child achievement monitoring system the planned results of the development of the Program should provide an integrated assessment approach final and intermediate Program development results, allow assessing the dynamics of children's achievements and include description of the object, forms, frequency and contentmonitoring.

The monitoring process examines the physical, intellectual and personal qualities

Planned time for a psychological and pedagogical diagnosis of the results of the development of the Program: 5-7 days in September and May.


Features of the organization of the educational process
The section describes the features of the organization of the educational process in the preschool educational institution, which ensure the achievement of the planned results of joint activities, for example:

In the mode of operation of a preschool educational institution; - in leading forms of conducting classes; - in the organization of the subject-development environment; - in the selection of personnel; - in the features of the organization and conduct of various events; - in the establishment of social partnership; - in interaction with the family; - in the traditions of a preschool educational institution, etc.

It is advisable to highlight those features of the kindergarten educational process that distinguish it from other preschool educational institutions.
For example, the organization of the work of groups separately for boys and girls; short stay, etc.

It is also recommended to note the additional educational services provided by the institution both within the framework of budgetary financing and on a paid basis, which reinforce the priority line of activity chosen by the kindergarten.


OOP Applications
- the composition of the working group on the development of EP; - work plan of the working group; - expert opinion on the OP; - Protocol of the pedagogical council on the approval of the OP; - an order on a preschool educational institution on the implementation of EPs indicating those responsible for certain areas; - plan for the implementation of the educational program of the DOE; - diagnostic techniques (“tool”) to section 6;

OOP Applications
Glossary of basic terms used by members of the teaching staff within the educational institution; - the results of diagnostics of the implementation of the educational program; - analytical materials substantiating the content of sections of the educational program; - analytical materials justifying the need for changes and additions to sections of the educational program.

Kornilova Marina Vladimirovna,
(once every six months or once a year) - this is a description of the dynamics of the formation of the integrative qualities of pupils of each age group for their development of the Program in all areas of children's development;
are monitoring results
it is carried out when a child is released from kindergarten to school and includes a description of the integrative qualities of a graduate of a preschool educational institution.
Held annually in the preparatory group for the school.
A portrait of a graduate can be drawn up by the teaching staff of the preschool educational institution, taking into account regulatory documents

Child achievement monitoring system the planned results of the development of the Program should provide an integrated assessment approach final and intermediate Program development results, allow assessing the dynamics of children's achievements and include description of the object, forms, frequency and contentmonitoring.

The monitoring process examines the physical, intellectual and personal qualities

Planned time for a psychological and pedagogical diagnosis of the results of the development of the Program: 5-7 days in September and May.


Features of the organization of the educational process
The section describes the features of the organization of the educational process in the preschool educational institution, which ensure the achievement of the planned results of joint activities, for example:

In the mode of operation of a preschool educational institution; - in leading forms of conducting classes; - in the organization of the subject-development environment; - in the selection of personnel; - in the features of the organization and conduct of various events; - in the establishment of social partnership; - in interaction with the family; - in the traditions of a preschool educational institution, etc.

It is advisable to highlight those features of the kindergarten educational process that distinguish it from other preschool educational institutions.
For example, the organization of the work of groups separately for boys and girls; short stay, etc.

It is also recommended to note the additional educational services provided by the institution both within the framework of budgetary financing and on a paid basis, which reinforce the priority line of activity chosen by the kindergarten.


OOP Applications
- the composition of the working group on the development of EP; - work plan of the working group; - expert opinion on the OP; - Protocol of the pedagogical council on the approval of the OP; - an order on a preschool educational institution on the implementation of EPs indicating those responsible for certain areas; - plan for the implementation of the educational program of the DOE; - diagnostic techniques (“tool”) to section 6;

OOP Applications
Glossary of basic terms used by members of the teaching staff within the educational institution; - the results of diagnostics of the implementation of the educational program; - analytical materials substantiating the content of sections of the educational program; - analytical materials justifying the need for changes and additions to sections of the educational program.

Kornilova Marina Vladimirovna,
Planned time for a psychological and pedagogical diagnosis of the results of the development of the Program: 5-7 days in September and May.


Features of the organization of the educational process
The section describes the features of the organization of the educational process in the preschool educational institution, which ensure the achievement of the planned results of joint activities, for example:

In the mode of operation of a preschool educational institution; - in leading forms of conducting classes; - in the organization of the subject-development environment; - in the selection of personnel; - in the features of the organization and conduct of various events; - in the establishment of social partnership; - in interaction with the family; - in the traditions of a preschool educational institution, etc.

It is advisable to highlight those features of the kindergarten educational process that distinguish it from other preschool educational institutions.
For example, the organization of the work of groups separately for boys and girls; short stay, etc.

It is also recommended to note the additional educational services provided by the institution both within the framework of budgetary financing and on a paid basis, which reinforce the priority line of activity chosen by the kindergarten.


OOP Applications
- the composition of the working group on the development of EP; - work plan of the working group; - expert opinion on the OP; - Protocol of the pedagogical council on the approval of the OP; - an order on a preschool educational institution on the implementation of EPs indicating those responsible for certain areas; - plan for the implementation of the educational program of the DOE; - diagnostic techniques (“tool”) to section 6;

OOP Applications
Glossary of basic terms used by members of the teaching staff within the educational institution; - the results of diagnostics of the implementation of the educational program; - analytical materials substantiating the content of sections of the educational program; - analytical materials justifying the need for changes and additions to sections of the educational program.

Kornilova Marina Vladimirovna,
Educational program MDOU № 5 "Dubok" stanitsa Arkhangelskaya
|
Section 1. Explanatory Note ………………………………………. | ||
|
1.1. Relevance …………………………………………………………… .. | ||
|
1.2. Description of the "graduate model" ………………………………………. | ||
|
1.3. Goals and objectives of the educational program .............................. | ||
|
Section 2. Educational programs and their methodological support …………………………………………………………………. | ||
|
2.1.Selection of programs and educational technology, their integration and methodological support ……………………. | ||
|
2.2. Building a holistic pedagogical process ............. .. | ||
|
Section 3. Organization of the educational process of the DOE …………………………………………………………………………… .. | ||
|
3.1. Design and planning of the current pedagogical activity ………………………………………………………………… | ||
|
Section 4. System for monitoring children's achievements of the planned results of mastering programs …………………………………………… | ||
|
Section 5. Conditions for the implementation of the educational program ………. |
Educational structure dow programs
Key Points Section 1. Explanatory Note 1.1. Relevance: -Age and individual characteristics contingent of children - Social order, educational needs of parents - Purpose of pre-school education, basic means of implementation - Priority areas of activity - Features of the educational process (national-cultural, demographic, climatic) - Principles and approaches to the formation of the program 1.2. Description of the "graduate model" 1.3. Objectives and objectives of the educational program Section 2. Educational programs and their methodological support2.1. The choice of programs and pedagogical technologies, their integration and methodological support. 2.2. Building a holistic pedagogical process.
Section 3. Organization of the educational process of the DOE.3.1. Design and planning of the current pedagogical activity. 3.2. The content of psychological and pedagogical work on the development of educational areas by children
Section 4. System for monitoring children's achievement of planned results of program development
Section 5. Conditions for the implementation of the educational program.
BASIC PROVISIONS OF THE EDUCATIONAL PROGRAM
1.1. Educational program MDOU № 5 "Dubok" Art. Arkhangelsk developed in accordance with paragraph 5 of article 14, paragraph 1 of article 9 of the Law Russian Federation “On Education”, the Model Regulations on Kindergarten and federal state requirements for the structure of the basic general educational program of preschool education.
1.2. Educational program MDOU № 5 "Dubok" st. Arkhangelsk was developed on the basis of approximate basic general educational programs for preschool education.
1.3. Educational program MDOU № 5 "Dubok" st. Arkhangelsk - a document defining the specifics of the organization of the educational process in Kindergarten, the content of education, the form of organization of activities of preschool children and is aimed at the formation of a common culture, the development of physical, intellectual and personal qualities, the formation of prerequisites learning activitiesensuring social success, preservation and strengthening of the health of preschool children, correction of deficiencies in the physical and mental development of children.
1.4. Educational program MDOU № 5 "Dubok" st. Arkhangelsk provides for the construction of a holistic pedagogical process, includes a set of educational areas that provide diversified development of children, taking into account their age and individual characteristics in the main areas: physical, social, moral, artistic, aesthetic, cognitive and speech.
1.5. Educational program MDOU № 5 "Dubok" st. Arkhangelsk covers all the main points of life of preschool children.
Department of Education of Moscow
Moscow Institute of Open Education
Moscow City Psychological and Pedagogical University
In accordance with the approval and enactment of the Federal state requirements for the structure of the basic general educational program of preschool education (Order of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation No. 655 of November 23, 2009), the form and structure are changing Educational program DOW of the city of Moscow.
Currently, based on federal requirements, the following are being developed:
An approximate basic general education program for preschool education;
An approximate basic general education program for pre-school education for children with disabilities.
Until these two programs are operational, these recommendations are temporary.
The educational program of the preschool educational institution is considered as a model for the organization of the educational process focused on the personality of the pupil and taking into account the type of preschool educational institution, as well as priority areas of activity.
The main general educational program of preschool education (hereinafter - the Program) is developed, approved and implemented in an educational institution on the basis of approximate basic general education programs for preschool education.
The program determines the content and organization of the educational process for preschool children and is aimed at the formation of a common culture, the development of physical, intellectual and personal qualities, the formation of the prerequisites for educational activities that ensure social success, preservation and strengthening of the health of preschool children, correction of physical and (or ) mental development of children.
Program should:
Comply with the principle of developing education, the purpose of which is the development of the child;
Combine the principles of scientific validity and practical applicability;
Meet the criteria of completeness, necessity and sufficiency;
To ensure the unity of the educational, developing and training goals and objectives of the process of education of preschool children, in the process of implementation of which such knowledge and skills are formed that are directly related to the development of preschool children;
To be built taking into account the principle of integration of educational areas in accordance with the age-related capabilities and characteristics of pupils, the specifics and capabilities of educational areas;
Based on a comprehensive thematic principle of building the educational process;
To provide for the solution of educational programs in joint activities adult and children and independent activities of children, not only in the framework of educational activities, but also during the conduct of regimen moments in accordance with the specifics of preschool education;
Assume the construction of the educational process on age-appropriate forms of work with children. The main form of work with preschool children and the leading activity for them is the game.
The DOE educational program consists of two parts:
1) the mandatory part;
2) the part formed by the participants in the educational process.
Mandatory part Programs should be implemented in any educational institution , working on the basic general educational program of preschool education. It ensures the achievement of pupils readiness for school, namely the necessary and sufficient level of development of the child for the successful development of the basic educational programs of primary education. In compensatory and combined groups, the compulsory part of the Program includes activities for the qualified correction of deficiencies in the physical and (or) mental development of children with disabilities.
II part of the program, formed by the participants in the educational process, reflects: 1) the species diversity of institutions, the presence of priority areas of activity, including ensuring equal starting opportunities for teaching children in educational institutionsfor sanitary-hygienic, preventive and wellness activities and procedures for the physical, social, personal, cognitive-speech, artistic and aesthetic development of children (except for activities for the qualified correction of deficiencies in the physical and (or) mental development of children with disabilities); 2) the specifics of national-cultural, demographic, climatic conditions in which the educational process is carried out.
TimeThe necessary for the implementation of the Program ranges from 65% to 80% of the time spent by children in groups with a 12-hour stay, depending on the age of the children, their individual characteristics and needs.
Volume the compulsory part of the Program is at least 80% of the time required for the implementation of the Program, and the part formed by the participants in the educational process is not more than 20% of the total volume of the Program.
The structure of the educational program DOE
Title page
1. The name of the DOW.
2. "I affirm: the head of the preschool educational institution ...".
3. “Adopted at a meeting of the scientific and methodological council (pedagogical council), small pedagogical council, date, protocol No..
4. “Agreed” (UO or CMC).
6. On the back of the title page the content (table of contents) of the educational program is given.
Explanatory note
The general educational program of DOU No. ______ provides the diversified development of children from ___ to ____ years of age, taking into account their age and individual characteristics in the main areas - physical, social-personal, cognitive-speech and artistic-aesthetic. The program ensures the achievement of pupils readiness for school.
The explanatory note shall be disclosed:
1. Age and individual characteristics of the contingent of children brought up in an educational institution, information on the qualifications of teaching staff and information on families of pupils.
The main priority areas in the activities of the educational institution are: (to formulate).
3. Goals and objectives dOE activities for the implementation of the main educational program are determined based on an analysis of the results of the previous teaching activities, the needs of parents, the society in which the preschool educational institution is located.
Considering that the institution has developed a “Program for the development of preschool education”, which defines conceptual ideas, a development strategy for the entire educational institution and the mechanisms for its implementation, the Program defines the goals and objectives of the organization of the pedagogical process for its participants (children, teachers, parents of pupils).
4. Features of the educational process.
We remind you that they can be: organizational, national-cultural, demographic, climatic, etc.
When organizing the educational process, the principles of the integration of educational areas (physical culture, health, safety, socialization, labor, cognition, communication, reading fiction, artistic creation, music) should be taken into account in accordance with the age capabilities and characteristics of the pupils. Indicate this position, as well as the fact that "the organization of the educational process is based on a comprehensive thematic principle with leading gaming activities, and the solution of program tasks is carried out in various forms of joint activity of adults and children, as well as in independent activities of children."
5. Principles and approaches to the formation of a general education program (open in accordance with the above). For example: “The content of the general education program complies with the main provisions developmental psychology and preschool pedagogy and ensures the unity of educational, developmental and educational goals and objectives. ”
1st part (required)
1. Organization of the mode of stay of children in preschool
In this section of the preschool educational institution, you must submit:
A flexible mode of activity depending on the social order of parents, the availability of specialists, teachers, medical workers, approaches to training and education of preschool children, to the organization of all types of children's activities;
Schedules of interaction between teachers, specialists and educators;
A model of the educational process using various forms and taking into account the time of year and age-related psychophysiological capabilities of children, the relationship of planned activities with the daily life of children in kindergarten (Appendix No. 3);
Tempering system;
2. The content of psychological and pedagogical work on the development of educational areas
This section includes materials related to the design, planning and organization of ongoing educational activities in all educational areas: physical education, health, safety, socialization, labor, cognition, communication, reading fiction, art, music . Each educational area can be presented in two tables: the first is a list of programs, technologies, manuals; the second is the selection of forms of organization of the educational process that correspond to the tasks and selected content. This section is specific for each Kindergarten and even for each age group, therefore, forms of educational activity can be included in the long-term plan for each educational field of knowledge in age groups. Given that each educational area has its own specifics, the teacher independently chooses the forms of educational activity of children. At the same time, the total amount of the compulsory part of the Program is calculated in accordance with the age of the pupils, the main directions of their development, the specifics of preschool education and includes the time allocated to:
Educational activities carried out in the process of organizing various types of children's activities (playing, communicative, labor, cognitive research, productive, musical and artistic, reading);
Educational activities carried out during sensitive moments;
Independent activity of children;
Interaction with families of children on the implementation of the basic general educational program of preschool education.
List of comprehensive programs
1. The program of education and training in kindergarten / p ed. M.A. Vasilieva, V.V. Gerbova, T.S. Komarova. - M.: Mosaic-Synthesis, 2007.
2. Origins: The basic development program of a preschool child / Scientific. ed. L.A. Paramonova, A.N. Davidchuk, K.V. Tarasova, etc. - M .: Karapuz, 1997.
3. Development Program / L. A. Wenger, O. M. Dyachenko, N. S. Varentsova, etc. - M., 1994; 1995.
4. Childhood: A program for the development and upbringing of children in kindergarten / V. I. Loginova and others. - M.: Childhood Press, 2010.
5. From childhood to adolescence: A program for parents and educators on the formation of health and development of children from 1 year to 7 years / T. N. Doronova and others. - M .: Education, 2001.
6. The program "Kindergarten - a house of joy" / N. M. Krylova, V. T. Ivanova. - Perm, 1990; 1991.
2.1. The content of psychological and pedagogical work on the development of the educational field " Physical education»
Objectives:the formation in children of interest and value attitude to physical education, harmonious physical development through the solution of the following specific tasks:
- development of physical qualities (speed, power, flexibility, endurance and coordination);
- accumulation and enrichment of motor experience of children (mastery of the basic movements);
- the formation of pupils' needs for physical activity and physical improvement.
Each teaching staff independently solves the question of in what form and how often the results of mastering by children the basic general educational program of preschool education will be evaluated.
The list of programs and technologies
The planned final results of mastering by the children of the main general educational program of preschool education should describe the integrative qualities of the child that he can acquire as a result of mastering the Program. We give an example in accordance with the FGTOP: - physically developed, mastered the basic cultural and hygienic skills. The child has formed the basic physical qualities and the need for physical activity. Independently performs age-appropriate hygiene procedures, complies with the elementary rules of a healthy lifestyle; - l fictitious, active. He is interested in the new, unknown in the world around him (the world of objects and things, the world of relations and his inner world). He asks questions to an adult, likes to experiment. Able to act independently (in everyday life, in various types of children's activities). In cases of difficulty, seek help from an adult. He takes a lively, interested part in the educational process; - emotionally responsive. It responds to the emotions of loved ones and friends. Empathizes with characters in fairy tales, stories, stories. Emotionally reacts to works visual arts, musical and artistic works, the world of nature; - mastered the means of communication and ways of interacting with adults and peers. The child adequately uses verbal and non-verbal means of communication, owns dialogic speech and constructive ways of interacting with children and adults (agrees, exchanges objects, distributes actions in cooperation). Able to change the style of communication with an adult or peer, depending on the situation; - able to manage their behavior and plan their actions on the basis of primary value ideas, observing elementary generally accepted norms and rules of behavior. The behavior of the child is mainly determined not by momentary desires and needs, but by requirements from adults and primary value ideas about “what is good and what is bad”. The child is able to plan his actions aimed at achieving a specific goal. Comply with the rules of behavior on the street (traffic rules), in public places (transport, store, clinic, theater, etc.); - able to solve intellectual and personal tasks (problems), age-appropriate. A child can apply independently acquired knowledge and methods of activity to solve new problems (problems) posed by both adults and themselves; depending on the situation, it can transform methods for solving problems (problems). A child is able to propose his own plan and translate it into a drawing, construction, story, etc .; - having primary ideas about himself, family, society, state, world and nature. The child has an idea of \u200b\u200bhimself, his own belonging, and the belonging of other people to a certain gender; on the composition of the family, kinship and relationships, the distribution of family responsibilities, family traditions; about society, its cultural values; about the state and its affiliation; about the world; - mastered the universal prerequisites for educational activity - the ability to work according to the rule and according to the model, listen to the adult and follow his instructions; - mastered the necessary skills. The child has the skills necessary for the implementation of various types of children's activities. The portrait of the graduate reflects the personality qualities of the child and the degree of their formation. 2nd part. Regional component.
The main goal of pre-school education in the city of Moscow is the realization of the right of every child to a high-quality and affordable education, providing equal starting conditions for the full physical and mental development of children as the basis for their successful education in school. The “Main directions of the Program for the development of pre-school education in the city of Moscow for 2008–2017” clearly outlines the tasks of two large projects, the implementation of which gradually includes all pre-school educational institutions in Moscow: Joint pilot project of the Moscow City Department of Education and UNESCO “Moscow Education: From Infancy to School”; The project "Kindergarten of the future." The regional features that must be taken into account when organizing the educational process in a preschool educational institution are the developed programs, teaching aids and recommendations on the areas of implementation of these two projects. In accordance with the order of the Department of Education of the city of Moscow of March 12, 2008. No. 82 “On the resource center in the framework of the joint pilot project in the field of upbringing and education of young children“ Moscow education: from infancy to school ”between the Department of Education of the city of Moscow and the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)” was an experimental site “Moscow education: from infancy to school” was created. Currently, 32 educational institutions are included in the structure of the site: 17 resource centers and 15 educational institutionsimplementing general educational programs of preschool education, representing all district educational systems. Currently, on the basis of an order from the Moscow City Department of Education, work is underway to implement a joint pilot project in early childhood education and education “Moscow Education: From Infancy to School” between the Moscow Department of Education and UNESCO. Within the framework of this project, 17 resource centers have been created and are active in the areas of projects:
1. “Kindergarten for all” - inclusive, integrative and special education for children from 2 months to 7 years. 2. “Bilingual child - a dialogue of languages \u200b\u200band cultures” - the organization of preschool education of children in the conditions of bilingualism and multilingualism in connection with the proclamation of 2008 as the International Year of Languages. 3. "Little geniuses" - intellectual development preschool children. 4. “We and nature” - early environmental education in connection with the United Nations Decade of Education for Sustainable Development (2005–2014).
To use the preview of presentations, create yourself a Google account (account) and log in: https://accounts.google.com
Slide captions:
Features of the structure of the basic educational program of preschool education in accordance with Federal state requirements for the structure of the basic educational program of preschool education
In recent years, there have been significant changes in the system of preschool education. In just 2 years, several significant regulatory documents appeared that defined new priorities for the development of preschool education.
Today, preschool educational institutions are working on the implementation of the basic general educational program, the purpose of which is to ensure the high-quality implementation of the program through the selection and creation of methodological support and changes in the structure of the educational process.
The main educational program of the DOE is a regulatory document preschool, characterizing the specifics of the content of education, the features of the organization of the educational process, the nature of the educational services provided.
compulsory part, formed by the participants of the educational process The main general educational program of preschool education 80% of the total program volume 20% of the total program volume 65% - 80% of the time of functioning of the preschool institution
The structure of the Program Chapter 2. Organization of the mode of stay of children in pre-school Chapter 3. The content of psychological and pedagogical work on the development of educational areas; Chapter 4. Content corrective work; Chapter 5. Planned results of mastering by children of the general educational program (intermediate and final assessments); Chapter 6. Monitoring system. Chapter 7. Conditions for the implementation of the program of a preschool educational institution. Chapter 1. Explanatory note I PART (obligatory) Title page I I PART (optional)
Cover sheet 1. The name of the DOW. 2. “I confirm: the head of the preschool educational institution ... ..” 3. “Adopted at the meeting of the pedagogical council, date, minutes No. ...” 4. “Agreed” (UO or others) 5. Year. 6. On the back of the title page the contents (table of contents) of OP.
Program structure Explanatory note The name of the DOW in accordance with the license. Age and individual characteristics of the contingent of pupils. Directions of development. The content of the educational process. Goals and objectives of the DOE. Features of the educational process. Principles and approaches to the formation of the educational program.
The main directions of development Cognitive and speech development Social and personal development Physical development Artistic and aesthetic development Physical culture Health Music Artistic work Communication Cognition Reading fiction Socialization Labor Safety Explanatory note
Approximate general educational program of preschool education * Defines the compulsory (invariant) part of the basic general educational program of preschool education, which should be implemented in any institution of preschool education that has state accreditation. * It is a basis for the content of preschool education and ensures that students achieve psychological and physical readiness for school. Explanatory note
The amount of educational load in the main areas of children's development in existing programs: cognitive and speech development, artistic and aesthetic development 20 - 40% physical development, social and personal development Explanatory note
The total amount of the mandatory part of the Program includes the time allotted for: NOD OD during regimen moments Interaction with families of children Independent activities of children Explanatory note
The basic general educational program for preschool education must comply with the principle of developing education; combine the principles of scientific validity and practical applicability; meet the criteria of completeness, necessity, and sufficiency; Ensure the unity of the educational, developmental, and educational goals and objectives of the educational process for preschool children. It is built taking into account the principle of integration of educational areas in accordance with the age-related capabilities and characteristics of pupils, the specifics and characteristics of educational areas Based on a comprehensively-thematic principle of building the educational process Provide for the solution of educational programs in conjunction with an adult and independent activities, as well as during regimen moments in in accordance with the specifics of preschool education. Build on age-appropriate forms of work with children in the form of games, conversations, readings, observations and others., through the organization of various types of children's activity and initiative, which is led from the game. Explanatory note
The content of psychological and pedagogical work on the development of educational areas by children. Design, planning and organization of ongoing educational activities in all educational areas includes: Goal, objectives; Model, chart or table for integration with other educational areas; Software; A table or chart on the implementation of educational areas in different forms of work, means, techniques, methods of working with children. Chapter 3
Calculation of the total volume of vocational education and training education for children and children under the age of 30 years. The structure of the educational process for children and children under the age of 6-7 years. The main part is 80% of the universities. -20%. The institution's working hours: 10.5 hours. Minutes: 630 minutes. General: 630 minutes. DO (sleep, supervision and care) 120 min Time for the implementation of PLO DO General: 510 min 80% 408 min 102 min NOD carried out in the process of implementing various types of children's activities General: 120 min 90 min 30 min OD carried out during regimen moments Total: 240 min (510-120-150) 192 min 48 min Independent activity of children General: 150 min 120 min 30 min Heads a 3.
Directions for the development of pupils Educational areas Leading activity Related activities Integration of educational areas Physical development Physical education Movement Game Communicative. Musical and artistic Cognitive and research Health Safety Music Communicative Cognition Health Gaming Motorized Communicative Cognitive and research Reading CL Labor Productive Physical culture Communicative Cognition Reading Labor Art. creativity The sequence of educational activities Chapter 3.
Planned results of mastering by children of the basic general educational program of preschool education include: final results, or a set of integrative qualities of children “at the exit” from the system of preschool education (social portrait of a 7-year-old child); intermediate results reflecting the age dynamics of the formation of integrative qualities of the child. Chapter 5
A monitoring system for children's achievement of the planned results of the Program development Should provide: a comprehensive approach to assessing the final and intermediate results of the Program development, allow assessing the dynamics of children's achievements and include a description of the object, forms, methods, frequency and content of monitoring Chapter 6.
this is the main part - this is part of the main general educational program of pre-school education, formed by the participants of the educational process in addition to the compulsory part, and reflecting: the species diversity of institutions (groups), the presence of priority areas of activity (except for activities for the qualified correction of deficiencies in physical and (or) mental development children with disabilities specifics of socio-economic, national-cultural, demographic, climatic and other conditions ovium in which the educational process is carried out c. I I PART PART VARIABLE PROGRAM STRUCTURE
Various options for correlation of the mandatory part of the Program and the part formed by the participants of the educational process The obligatory part + part formed by the participants of the educational process, reflecting the specifics of the conditions for its implementation. The compulsory part + the part formed by the participants in the educational process, reflecting: 1) the specifics of the conditions for its implementation; 2) priority area of \u200b\u200bactivity. The compulsory part + the part formed by the participants in the educational process, reflecting: 1) the specifics of the conditions for its implementation; 2) priority areas of activity; 3) implementation of the program of additional education.
Conditions for the implementation of the educational program of the DOE include: Management of the implementation of the Program; Creation and updating of the subject-development environment; Innovative or experimental work; Forms of cooperation with the family; Continuity in the work of DOW and schools; Dow interaction with other institutions. Chapter 7
The following sections will be individual for each Kindergarten: Explanatory note Organization of the regime of stay in Kindergarten Contents of correctional work Monitoring system Unified sections will be: Contents of psychological and pedagogical work on the development of educational areas Planned results for children to master the basic general education program of preschool education
Thanks for attention!
- The training system according to the Dalton plan - the organization of the educational process - Sergei V. Sidorov
- Internal differences, specialization of individual cities
- Consonant and letter th
- Not a single word: whom to work after philology
- Warning flags on the beach
- Abstract of speech therapy classes in elementary school
- Sound and Alpha Word Analysis

 Live journal
Live journal Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter