What consonant sound is indicated by two different letters. Next: Sounds Designation of sounds on the letter Sounds

MBDOU MO Krasnodar
"Kindergarten number 163"
Sound analysis of words.
"Crib for parents"
Shaking T.S.
for parents
Dear Parents!
Teaching a child to read and develop phonemic hearing, it should be remembered that:
Our speech consists of sentences.
A sentence is a complete thought.
Sentences are made up of words.
Words are made up of syllables. There are so many words syllables, how vowels letters (sounds), for example: ma/ li / na - in this word 3 syllable, since it has 3 vowels (sound).
Words are made up of sounds.
Sound is what we hear and pronounce.
The letter is what we write and read.
The sound on the letter is indicated by the letter.
Sounds are vowels and consonants.
Vowel sounds are sounds that can be sung in a voice (above-below), while the air coming out of the mouth does not encounter an obstacle.
There are six vowel sounds in Russian: A, U, O, I, E, S. In the diagrams, vowels are indicated in red. There are ten vowels: six - A, U, O, I, E, S - correspond to sounds and four - iotated, which mean two sounds: I, Yu, E, E, (I - YA, Yu - YU, E - IE, YO - YO) at the beginning of the word (pit, yula); after the vowel sound (lighthouse, zashushka); after soft and hard signs (family, rise). In other cases (after consonants) iotated vowels on the letter indicate the softness of the consonant in front of the vowel and the vowel: I - A. Yu - U, E - E, E - O (birch, ball). The vowels A, O, Y, S, E on the letter indicate the hardness of the consonants.
Consonant sounds are sounds that cannot be sung, because the air coming out of the mouth when pronouncing it encounters an obstacle.
The deafness and sonority of consonants is determined by the work of the vocal cords and checked by the hand laid on the throat: deaf consonants - the vocal cords do not work (the neck does not tremble): K, P, S, T, F, X, C, H, W, U; voiced consonants - the vocal cords work (the neck trembles): B, C, D, D, F, 3, Y, L, M, N, P
Always voiced (unpaired) consonants: Y, L, M, H, R. Always deaf (unpaired) consonants X, C, H, U. The remaining consonants form pairs:
B C D E F G H I - BELLS
P F K T Sh S - DEAF
The hardness and softness of consonants is determined by ear:
consonants sounds that can be hard and soft: B, C, D, D, 3, K, L, M, H, R, C, T, F, X, B, B, B, B, B, B, B, L, B, B, B , B, b, b, b, b;
always firm consonants: W, W, C;
always soft consonants: Y, H, S.
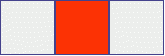
Solid consonant sounds in the diagrams are indicated in blue, soft consonants in green.
One of the important tasks of preparing for literacy is to familiarize children with the sound composition, sound structure of the word. The initial principle of the preschool literacy system is that the child’s acquaintance and work with letters must be preceded by a pre-genuine, purely sound period of instruction. A letter is a sign of sound.
Acquaintance with a letter sign will be inconclusive if the child does not know what exactly is indicated by this sign. The pre-literary stage of literacy takes a lot of time and effort. But one should not strive to reduce it - after all, the success of the further formation of the reading skill depends on the pre-early stage of training. If, even in the pre-quaternary period, the child learns to freely move from a solid consonant sound to his soft pair and vice versa, then later the most difficult step will not cause difficulties for him elementary education Reading is the merging of two letters into a syllable. Knowing letters without a sense of sound is the same as knowing the names of colors in color blindness. And it is no coincidence that children with excellent memory and a little ambitious parents sometimes recognize and name all the letters by the age of two, but even by the age of seven they do not begin to add them if they are not familiar with the sounds. Successful speech development in preschool age is crucial for the subsequent systematic study of the mother tongue. D.B. Elkonin wrote that the reader operates on the sound side of the language, and reading is the process of reconstructing the sound form of a word according to its graphic (letter) model. This implies the need for a preliminary acquaintance of children with a wide sound reality. The child is surrounded by many sounds: music, the twittering of birds, the rustling of grass, the sound of the wind, the murmur of water ... But speech words sounds - from his very birth are the most significant.
Sounding speech provides the child with the necessary communication with adults, receiving information, getting involved in activities, and mastering the norms of behavior. The purity of speech depends on many factors: on the development of speech hearing, speech attention, speech breathing, voice and speech apparatus.
Teaching children sound analysis of words begins with determining the sequence of sounds in it. You need to identify the sequence of sounds by repeatedly pronouncing the word with a consistent intonational emphasis of each sound. So, when analyzing the word beetle, the child must say it three times:
zhzhuk, zhuuuk, beetle.
Children cannot master sound analysis by just saying the words out loud. It is necessary to show them the word objectively, presenting its sound structure in the form of a model.
Really present the word gives the opportunity a picture-scheme of its sound composition. It contains a drawing-object, the name of which the child must make out and a number of cells under the picture, which are successively filled with chips.

The word model that results from sound analysis reflects individual sounds and their sequence. When conducting sound analysis, the child leads with a pointer under the diagram and, in accordance with the movement of the pointer, pronounces a word with sequential allocation of sounds, designating each of them with a token.
Familiarization with vowel sounds.
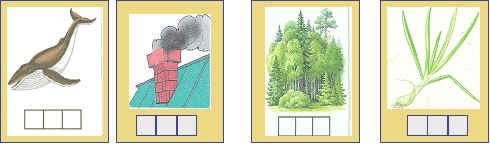
Children learn that sounds, during the formation of which air flows freely, nothing "interferes" with these sounds - neither teeth, nor lips, nor tongue, are called vowels. Children find such sounds in previously analyzed words: poppy [a], bow [u], home [o], forest [e], whale [i], smoke [s]. To make sure their conclusions are correct, the children “check” all the sounds, pronouncing them, and watch to see if anything in the mouth interferes with their pronunciation. Vowel sounds are denoted by a red token.
|
[g] [y] [smiling] [and] |
Familiarization with hard and soft consonants.
Sounds, during the formation of which air does not pass freely, encounters obstacles, something “interferes” - lips, teeth, tongue, are called consonants. A solid consonant sound will be denoted by a blue chip,and a soft consonant is a green chip.


Familiarization with stressed vowels.
After the pupils learn to distinguish between vowels, hard and soft consonants, it is necessary to familiarize them with the stress, to teach them to emphasize the stressed syllable and stressed vowel in the word. then move on to words with emphasis on the second syllable. Learning the ability to isolate verbal stress is included in the work of conducting sound analysis. Following the stressed syllable, children get acquainted with the stressed vowel sound. A black color is used to indicate the stressed vowel sound.
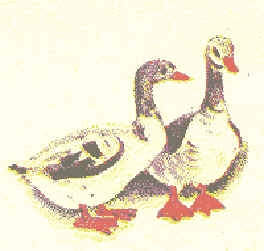
Run sound analysis goose words

![]()
What are the vowels? ([y], [and])
How many syllables in a word? (Two)
Name them. (GU-SI)
What is the stressed syllable? (PG)
Say the word with emphasis. (GUUUSI)
IN stressed syllable pronounced vowel. (UUU)
We read the word with stress, leading the pointer under the diagram.
Adult pronounces GUSII.
What sound is highlighted? (AND)
How to say it right? GUUUSI.
The vowel in the stressed syllable is called the stressed, which is pronounced more lingeringly.
It is important that the child learns what the sound of speech is, can differentiate sounds, divide words into sounds and syllables. Only then can he easily master the reading skill.
Letters are a graphic symbol of sounds. Often we are faced with the fact that children are taught letter-by-letter reading, i.e. children, seeing a letter, pronounce its name, not the sound. The result is “kaote,” instead of “cat.” Children have difficulty understanding the rules for voicing letters and combinations of letters. This creates additional difficulties in teaching children to read.
In the methodology of teaching reading to kindergarten provides for the naming of letters according to their sound designations: n, b, k .... This greatly facilitates reading skills for children.
Sound and letter: sound - unit sounding speech, and the letter is a graphic sign to indicate the sound of speech on the letter.
Sounds are pronounced and heard, and letters are written and read. Sounding speech is a natural way of existence of a language, its material expression, and writing is an artificial, human-made means of fixing, recording sounding speech with the help of graphic signs. Sounds are in any language, regardless of whether there is a written language in this language, since the sounding speech is primary in relation to the letter.
So, the sounding speech is fixed on the letter with the help of letters. It is assumed that each sound should have its own graphic designation - a letter. So, for example, the word home consists of three sounds - [d], [o], [m] - and on the letter, respectively, is a sequence of three letters - d, o, m. If each pronounced sound is recorded in a separate letter , then the basis of writing is the phonetic principle - "I write as I hear." However, it is obvious that Russian writing is arranged differently (see Principles of Russian Spelling).
It is difficult to find two completely identical sounds in Russian sounding speech: sounds can noticeably change depending on the position (for example, vowels under stress and in unstressed position, consonants in the position of the end of a word), they can also change under the influence of neighboring sounds (voicing of deaf consonants before voiced, stunning voiced consonants before the deaf). However, in writing, these different sounds are often indicated by a single letter. For example, in the word cat we hear the sound [o] and write the letter o, and in the word cat we pronounce and hear the sound [a] in the root, but we write the same letter about. Or at the end of the word pond, we write the letter q, although we do not pronounce the sound [q], as in the word of the pond, but the sound [t].
Sometimes, on the contrary, we designate identical sounds with different letters. For example, in the first pre-stressed syllable of the words forest, fox, knitted, we pronounce and hear the same sound, but in the letter we use different letters: e, and, i.
In addition, sometimes a letter denotes two sounds: I, Yu, etc., and sometimes one sound is transmitted by the letter combination: eh [l ’]. There are letters that do not reflect any sound at all: a hard sign b and a soft sign b. Material from the site
So, it is obvious that the relationship of sounds and letters can sometimes be very complex. It is clear that not every sound of speech should be indicated on the letter with a special letter, because in that case there would be a lot of letters. However, in any language there are certain sounds that are extremely important for the language, and these sounds must necessarily be reflected in the letter. Such sounds perform a meaning-distinguishing function and are called phonemes (see. Phoneme). Russian letter almost entirely built on the phonemic principle, that is, the letters you reflect on the letter are not sounds, but phonemes (see. Principles of Russian spelling).
Ideally, if the alphabet reflects the phonemic composition of the language, that is, for each phoneme there is a special letter. The absence of special letters for phonemes creates enormous difficulties, therefore the alphabet of one language has to be specially adapted to the system of another language (see. Graphics).
Did not find what you were looking for? Use the search
When pronouncing the alveolar arched consonants [n, l, t, d], the tip of the tongue touches the alveoli (tubercles behind the upper teeth). These sounds are not softened before the vowels and at the end of the word. To avoid an undesirable vowel overtones, you do not need to strongly press the tip of the tongue and hold it for a long time on the alveoli. The deaf consonant [t] at the beginning and at the end of words is pronounced vigorously. In Russian, such sounds are made by touching the tip of the tongue of the upper teeth, and not the alveoli. Compare:
[n] - [n] no - net (grid) [l] - [l] forest - less (less) [t] - [t] type - tip (tip) [d] - [d] gave - dull ( boring)
In a letter, the sounds [n, l, t, d] are respectively indicated by the letters: Nn [en] Ll [el], Tt [ti:], Dd [di:]: net, less, tip, dull.
Sounds [s, z]
English consonants [s, z] are called slotted, because when they are pronounced between the tip of the tongue and the alveoli, a gap is formed through which air passes. When pronouncing English slotted sounds [s, z], the tip of the tongue is raised to the alveoli, but does not touch them. The voice passes through the gap formed between the alveoli and the tip of the tongue. When pronouncing Russian slotted consonants, the tongue is at the base of the lower teeth.
Compare:
On the letter, the sounds [s, z] are indicated by: - \u200b\u200bletters Ss [es]: some, start, Zz [zed]: zebra, Zena - a combination of letters ss [dʌbl es]: less - letter Cc [si:] before the vowels e, i, y: center, city, cycle.
Compare Russian and English consonants:
|
English |
English |
|||
Sound [e]
When pronouncing a short vowel [e], the tip of the tongue is at the base of the lower teeth. The lips are slightly stretched. The English sound [e] is similar to the Russian sound [e] in the words "these, chains." Before deaf consonants, [e] is pronounced very briefly, and before consonants, [n, l, m] is noticeably lengthened.
Compare the pronunciation of Russian and English words.
When pronouncing the sound [e], be guided by the sound [e] in the words "these", "chains".
[bed] troubles - bed (bed) [beg] run - beg (beg) [les] forest - less (less) [spel] sang - spell (spell) [net] no - net (network) [smel] dare - smell (smell) [test] test - test (test, test) [tekst] text - text (text)
This is how [e] sounds in English words.
[pen] pen - pen [desk] desk - desk [bed] bed - bed [tekst] text - text [lesn] lesson - lesson [nekst] next - next [end] end - end [tent] tent - tent
On the letter, the sound [e] is indicated by the letter Ee [i:] if one or more consonants follow: pen, bed, tent, egg, desk, end, next.
When we speak, we make sounds. They are formed as a result of the movement of air from the lungs through the mouth and, depending on how the tongue and lips are located at this moment, have a different color.
Sounds of speech participate in the formation of words - language units that have a certain semantic meaning and are used for the communication process. Let's get to know them better!
What are letters and sounds
Everything we hear and say is sounds. They are indicated in a certain way on the letter, and what we write and then read is letters.
But the sounds of speech and the letters by which they are indicated in the Russian language vary greatly in quantity. In spoken language, we pronounce 43 basic sounds, but we use only 33 letters to write them.
That is, all the letters of our language can be divided into 3 groups.
- Letters that do not indicate sounds (these are “b” and “b”). As an example, you can cite: “stump”, which is pronounced [p´en´], and “move out” - [sy´ehat´].
- Letters denoting 2 sounds. Such letters include "e", "e", "y", "I". In their pronunciation a pair of sounds is used: [yo], [yo], [yo], [ya].
- The letters that indicate 1 sound (these are all the other letters).
What is the difference between vowels and consonants
There are two main groups of speech sounds - they are defined as Vowels are those sounds in which only the voice is involved. They are pronounced lingeringly, in the mouth the sound does not meet any barriers.
Consonants - this is what we pronounce, combining both voice and noise (they are called voiced) or only noise (deaf consonants). In addition, consonants can be either hard or soft. 
Stressed and unstressed syllables
Vowels of speech participate in the formation of syllables, while being under stress or in an unstressed position. Stress means the pronunciation of a syllable with greater force.
The Russian language is characterized by a change in the position of stress. It can appear on any syllable, unlike the Polish or French languages, where a certain place is assigned to it. For example, in the word "whistled" the stress on the first syllable, and in the word "whistle" - on the second.
What letters indicate vowel sounds in Russian
To indicate the main vowel sounds of speech (there are six in our language), ten are used:
sound [and] - is indicated by the letter “and” (tiger);
[s] - the letter "s" (smoke);
[a] - the letters "a" (mother) and "I" (pit);
[o] - the letter “o” (nose) and “ё” (hedgehog);
[e] - the letter "e" (echo) and "e" (day);
[y] - with the letter “u” (kum) and “u” (south).
Thus, it turns out that in order to denote 4 vowels ([o], [a], [e], [y]) in the alphabet there are two whole rows of letters. It can be:
- a, o, e, y;
- i, e, e, y.
In the second row, letters perform two functions at once. They not only indicate but also signal that the previous consonant was soft (chalk - [m´el]).
If they are at the beginning of a word, located after vowels or after a soft or hard dividing sign - they indicate a combination of sounds. For example, the word Christmas tree sounds [yolka], and the word sings - [pay´ot]. 
As indicated on the letter
Sounds of speech participate in the formation of words and are there in a weak or strong position, which often has a direct effect on their designation in writing. So, with the same letter in the language can be denoted different sounds. Example: the letter “n” can denote 2 sounds - [n] and [n´]: niche - [n´isha] or null [null].
And one letter “b” can mean 4 variants of sounds [b], [b´] or [n], [p´]. For example: there was [was] - beat [b´il] or hump [hump] - Ob [op´].
If the voiced consonant is written at the end of the word or is placed before the deaf consonants, then it can indicate its paired deaf sound. This position is called weak. Pay attention to how we pronounce: kadka - ka [t] ka (sound is in front of a deaf consonant) or eye - gla [s] (sound is at the end of a word). This process is defined as stunning.
Deaf consonants may sound like their paired - voiced if they are in a strong position. For example: threshing sounds like a milk [d´] ba, and in the request word is heard the sound [z´] - about [z´] ba. This, as you know, is a blessing.
It should be noted that in Russian the position of consonants before vowels or before voiced consonants is considered a strong position in Russian. 
As the letter indicates some consonant sounds
Some sounds of Russian speech are indicated on the letter by a combination of letters. By the way, this situation causes a very large number of spelling errors.
For example, a single sound [щ´] in a written word may look like mid, zh or zh. We write - the score, but we pronounce [shchot], we write - the cabman, and we say [izvoshchik], we write - the man, but it sounds like [muschina].
And the sound [ts] can be designated both as a combination of ts or dts, and as ts or tf. For example: read - read [q] a, twenty - two [q] at.
Letters do not always correspond to “their” sounds
As already mentioned, the sounds of speech participate in the formation of words and are indicated in letters by certain letters. And it often turns out that different sounds can “hide” behind one letter. For example, in the root of a word, when its number changes, we write the same letter, but pronounce different sounds at the same time: TABLES (st [o] l) - TABLES (st [a] ly). That is, with one letter “o” we mean two sounds: [o] and [a].
But there are cases when different sounds are indicated by one letter. So, in the word “treasure” and in the word “raft” at the end one and the same sound sounds [t], but it is indicated, as you see, in different letters: "D" and "t".
The literal composition of words often does not coincide with the sound. For example, in the word “valiant” ten letters are written, but only nine are pronounced: [valorous “word”]. In this and similar cases, the letter "t" is an unpronounceable consonant. That is, a letter that does not mean sound. Here are a few more examples of such letters: the sun - [sonce], the heart - [s'erze].

Features of the combination of consonants and vowels
Hard Russian speech cannot be combined with the vowel “and” following them, and soft ones cannot be combined with “s”. For example, in the word “dinner” always solid sound [g] requires sound [s] so we pronounce [uzhyn].
In some cases, softening occurs in speech of hard consonants, paired with soft. So, if in a word a carriage, the sound [n] is solid, then in combination with the always soft [h´] it sounds softly - the car [car ”chchik].
The same thing happens in situations with a combination with other soft consonants: fantasy - fa [n´t´] ik, forest - le [s´n´] ik, pure - chi [c´t´] it.
The use of solid and in Russian
The sounds of speech and letters in our language, as you probably already understood, often do not match. So, for example, solid and soft sign the letter does not indicate any sounds.
These letters, as a rule, signal that the letters e, e, i, y behind them are pronounced as two sounds (drinks [pyot]). If b is after the consonant, then it indicates its softness (day [d´en´]).
In some cases, a soft sign plays only a grammatical role. For example, in the word “lie” it does not mean the softness of the previous consonant, but only indicates that the noun belongs to the female gender. 
Features of the spelling and pronunciation of some borrowed words
In some words borrowed from other languages, the letter e does not sound soft, as is customary in Russian, but a solid consonant. Pay attention - in the word "pace" we write e, but at the same time we pronounce a solid sound [t]. The pronunciation of this and similar words needs to be memorized or refer to the orthoepic dictionary.
Kashne - [ne], model - [de], claim - [te], relay - the first syllable [re], dash - [re], test - [te], thermos - [te], tennis - [te].
As you can see, the sounds of speech (Grade 1 or 11 are left behind) is a deep and serious topic that, when carefully studied, will help you understand the intricacies of pronunciation rules and the principles of writing many words that cause difficulties. Good luck
- The training system according to the Dalton plan - the organization of the educational process - Sergei V. Sidorov
- Internal differences, specialization of individual cities
- Consonant and letter th
- Not a single word: whom to work after philology
- Warning flags on the beach
- Abstract of speech therapy classes in elementary school
- Sound and Alpha Word Analysis

 Live journal
Live journal Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter