The main sections of the educational program dow. The approximate total volume of the part formed by the participants of the educational process. establishment of market relations, including in the social sphere, and, as a result, competition of educational institutions

To use the presentation preview, create a Google account (account) for yourself and log in: https://accounts.google.com
Captions for slides:
Features of the main structure educational program pre-school education in accordance with the Federal State requirements for the structure of the basic general educational program of pre-school education
In recent years there have been significant changes in the system of preschool education. In just 2 years, several significant regulatory documents have emerged that define new priorities for the development of pre-school education.
Today, DOUs are working on the implementation of the basic general education program, the purpose of which is to ensure the quality implementation of the program through the selection and creation of methodological support and changing the structure of the educational process.
The main general educational program of pre-school is a regulatory and management document of a pre-school institution, which characterizes the specifics of the content of education, features of the organization of the educational process, the nature of educational services provided.
compulsory part part formed by the participants of the educational process The main general educational program of preschool education 80% of the total Program 20% of the total Program 65% - 80% of the time of the preschool institution
Program Structure Chapter 2. Organization of the regime for children in preschool; Chapter 3. The content of psychological and pedagogical work on the development of educational areas; Chapter 4. Contents remedial work; Chapter 5. The planned results of the development of children's general education program (interim and final assessment); Chapter 6. Monitoring System. Chapter 7. Conditions for the implementation of the program of preschool educational institutions. Chapter 1. Explanatory note I PART (obligatory) Title page I I PART (optional)
Title page 1. Title DOW. 2. “I approve: the head of the DOE ... ..” 3. “Adopted at the meeting of the pedagogical council, date, protocol No. ...” 4. “Agreed” (PP or others) 5. Year. 6. On the back of the title page content (table of contents) OP.
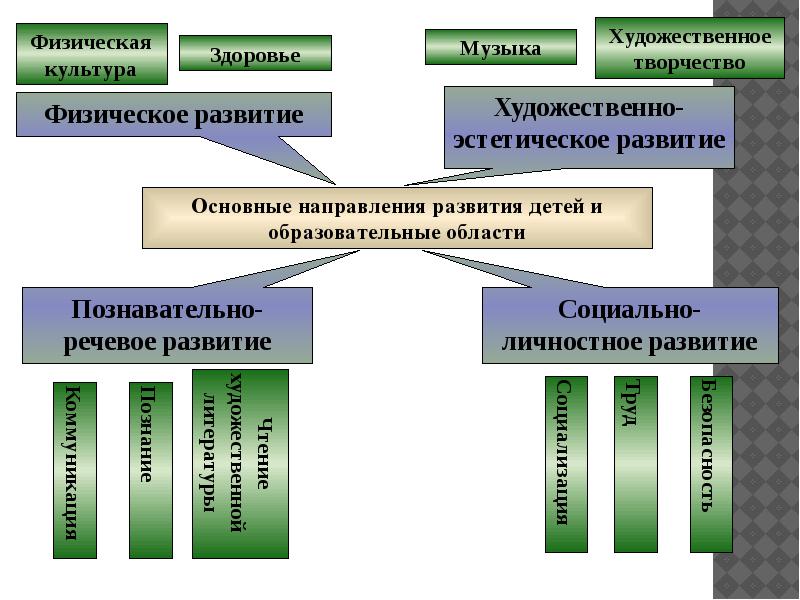
Program Structure Explanatory note DOW name in accordance with the license. Age and individual characteristics of the contingent of pupils. Directions of development. The content of the educational process. Goals and objectives of the activities of the DOW. Features of the educational process. Principles and approaches to the formation of the educational program.
The main directions of development Cognitive and speech development Social and personal development Physical development Art and aesthetic development Physical education Health Music Artistic works Communication Cognition Reading fiction Socialization Labor Security Explanatory note
Approximate general educational program of pre-school education * Determines the mandatory (invariant) part of the basic general educational program of pre-school education, which should be implemented in any pre-school education institution that has state accreditation. * It is the basis of the content of pre-school education and ensures that pupils achieve psychological and physical readiness for school. Explanatory note
The volume of educational load on the main directions of development of children in existing programs: cognitive and verbal development, artistic and aesthetic development 20 - 40% physical development, social and personal development Explanatory note
The total amount of the obligatory part of the Program includes the time allotted for: GCD ML during security moments Interaction with families of children Independent activity of children Explanatory note
The basic general educational program of pre-school education must comply with the principle of developmental education Combine the principles of scientific validity and practical applicability Comply with the criteria of completeness, necessity and sufficiency Ensure the unity of educational, developmental and teaching goals and objectives of the process of education of children preschool age. It is built taking into account the principle of integration of educational areas in accordance with the age possibilities and characteristics of pupils, the specifics and features of educational areas. Be based on the complex-thematic principle of the educational process. Consider solving educational program problems in conjunction with adults and independent activities, and accordance with the specifics of preschool education Build on age-appropriate forms of work with children in the form of games, conversations, readings, observations and others., through the organization of various types of children's activity and initiative, which is led from the game. Explanatory note
The content of psychological and pedagogical work on the development of children's educational areas. Design, planning and organization of the current educational activities all educational areas include: Goal, tasks; Model, scheme or table for integration with other educational areas; Software; Table or scheme for the implementation of educational areas in different forms of work, tools, techniques, methods of working with children. Chapter 3
The calculation of the total volume of OCH OOP TO and ChFUOP The structure of the educational process OOP TO The age of children 6-7 years old The main part - 80% ChFUOP -20% Office hours: 10.5 hours Minutes: 630 minutes Total: 630 minutes Time when the PLO is not implemented TO (sleep, supervision and care) 120 min Time for the implementation of the OOP to General: 510 min 80% 408 min 102 min NOD, carried out in the process of implementing various types of children's activities Total: 120 min 90 min 30 min OD, carried out during the regime moments General: 240 minutes (510-120-150) 192 minutes 48 minutes Children’s independent activities General: 150 minutes 120 minutes 30 minutes Heads a 3
Directions of development of pupils Educational areas Leading activity Related activities Integration of educational areas Physical development Physical culture Motive Game Communicative. Music and Art Cognitive-research Health Safety Music Communicative Cognition Health Gaming Motor Communicative Cognitive-research Reading CL Labor Productive Physical Culture Communicative Cognition Reading Labor Arts. creativity The sequence diagram of educational activities Chapter 3.
The planned results of the children’s mastering of the basic general educational program of preschool educational institutions. Include: final results, or a set of integrative qualities of children “at the exit” from the system of preschool education (social portrait of a 7-year-old child); intermediate results, reflecting the age dynamics of the formation of the child's integrative qualities. Chapter 5
The system for monitoring the achievement of the planned results of the Program implementation by children Must provide: a comprehensive approach to assessing the final and intermediate results of the Program implementation, allow for the assessment of the dynamics of children's achievements and include a description of the object, forms, methods, frequency and content of monitoring Chapter 6.
this is the main part - it is part of the main general educational program of preschool education, formed by the participants of the educational process in addition to the obligatory part, and reflecting: the species diversity of institutions (groups), the presence of priority activities (except for activities on the qualified correction of deficiencies in the physical and (or) mental development children with disabilities, the specifics of the socio-economic, national-cultural, demographic, climatic and other conditions in which the educational process takes place c. I I PART. Variable Program Structure
Different versions of the correlation of the mandatory part of the Program and the part formed by the participants of the educational process Mandatory part + part formed by the participants of the educational process, reflecting the specific conditions of its implementation. Obligatory part + part formed by the participants of the educational process, reflecting: 1) the specifics of the conditions for its implementation; 2) priority activities. Obligatory part + part formed by the participants of the educational process, reflecting: 1) the specifics of the conditions for its implementation; 2) priority activities; 3) the implementation of an additional education program.
Conditions for the implementation of the pre-school educational program include: Managing the implementation of the Program; Creation and updating of the subject-developing environment; Innovative or experimental work; Forms of cooperation with the family; Continuity in the work of pre-school and school; Dow interaction with other institutions. Chapter 7
The following sections will be individualized for each preschool: Explanatory note Organization of a stay in a pre-school The content of correctional work Monitoring system The following sections will be unified: Content of psychological and pedagogical work on the development of educational areas Planned results of children’s mastering the basic general educational program of preschool education
Thanks for attention!

The structure and content of the educational program of pre-school
New approaches to management in the system of preschool education cause a change in the range of functions, principles, methods and techniques of management activities of heads of educational institutions. These changes are objective and are caused by the following main factors:

main factors:
the development of market relations, including in the social sphere, and, as a result, the competition of educational institutions;
the establishment of an alternative system of support for preschool children in the form of government and private educational institutions;

main factors:
the departure from the unified program in the field of pre-school education and the presence of a fan of curricula, aids, and didactic materials;
lack of regulatory funding for pre-school educational institutions;
opportunities to attract extrabudgetary funds to institutions;

main factors:
parental interest as the main social customers in the productive activities of a particular educational institution;
the desire of the public to influence the educational process in the institution, etc.

The optimal mechanism for ensuring these processes is the activity of the pre-school educational institution in developing and implementing its own basic General Education Program (OOP)

The basic general education program (OOP) is a mandatory regulatory document developed and implemented, in accordance with paragraph 5, art. 14 of the Law of the Russian Federation "On Education", "each educational institution independently"

Order of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation of November 23, 2009 N 655 "On approval and implementation of federal state requirements for the structure of the basic general educational program of preschool education"

OOP preschool educational institution is one of the main regulatory documents governing its livelihoods.
Along with the Charter, it serves as the basis for accreditation, changes in budget financing, organization of paid educational services in accordance with the social order of parents (legal representatives).

The main educational program of preschool educational institutions -
regulatory document justifying the choice goals content used techniques and technologies, forms organization of the educational process in each specificpreschool educational institution

PLO DOW is considered as a model of the organization of the educational process of a personality-oriented pupil and taking into account the type of pre-school educational institution, as well as priority activities

PLO and Charter
The Charter is a legal document, a kind of constitution of an educational institution. It defines the features of the functioning of the entire educational institution as a whole.
OOP determines the content of the educational process, standardizing its components in detail.

OOP and educational standards
Temporary standards for pre-school education define the mandatory part of pre-school education and the requirements for the level of assimilation of this content.
A means of implementing the standard is a combination of basic and partial programs, developed by each educational institution individually and recorded in the PLO.

OOP and development program
PLO is aimed at the realization of the goals of education, development and training of children, that is, the successful implementation and development of the pedagogical component of an educational institution directly
A development program is a variety of targeted programs. Unlike OOP she not required regulatory document for educational institutions and is aimed primarily at solving the most pressing problems of the entire educational institution as a whole, affecting all aspects of its life activity: economic, regulatory, material and technical, etc.

OOP and educational institution concept
The concept is an integral, necessary part of the development program. It is a system of values and norms that the pedagogical staff of an educational institution chooses for itself and which it intends to use in its professional activities.
The PLO appears in this case as a complex condition for the implementation of the concept.

OOP and experimental work program
OOP in this case is one of the options for the organizational design of the experimental work
If the DOU is an experimental platform of any level, then it, together with the supervisor, develops an experiment program that includes the rationale for the problem, the research hypothesis, the definition of the object and subject of work, the theoretical analysis of the basic concepts, as well as the methodological part. It is aimed at determining the effectiveness of certain innovations.

OOP and state accreditation procedures
In this case, the educational program of the preschool educational institution is the basis and the basis for the qualitative and successful completion of the designated procedure.
If, as a result of the planned development, an educational institution wants to change its status, then based on the developed and implemented general education program, in which the desired status (type and type) must already be indicated, it will, in accordance with the approved procedure, undergo a state procedure accreditation and subsequently, according to its results, this or that status is obtained.

Thus, the process of developing and implementing OOP can be viewed as a process of harmonizing state educational standards, a social order to a specific educational institution, and its pedagogical capabilities.


Clause 4 Article 7 of the Federal Law "On Education"
Under "The structure of the main educational programs" understand the ratio and volume of their parts, as well as the ratio of the mandatory part of the main educational program and the part formed by the participants of the educational process.

The recommended structure of the PLO preschool educational institutions
Mandatory part Programs
The second part (variable)Programs formed by participants of the educational process
Applications to the program.

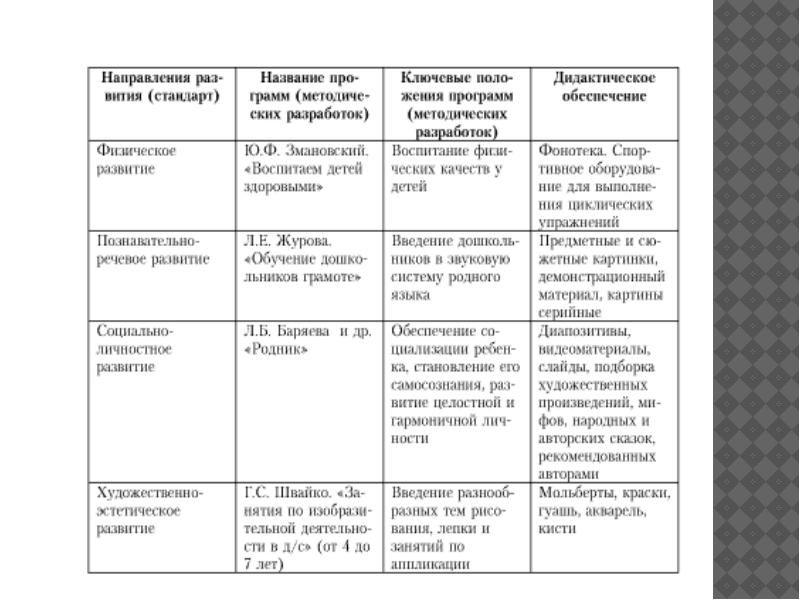
Analysis of existing (integrated) programs
The program of education and training in kindergarten/ Ed. M.A. Vasilyeva, V.V. Gerbovoy, TS Komarova (2005 version).
Rainbow: Program of upbringing, education and development of preschool children in kindergarten conditions / Т.N. Doronova, S.G. Jacobson, E.V. Solovyov and others; Scientific hands T.N. Doronova.
Childhood: Program of development and education of children in kindergarten / V.I. Loginova, T.I. Babaeva, N.A. Notkina et al .; Ed. T.I. Babaeva, Z.A. Mikhailova, L.M. Gurovich,
The approximate educational program of education, training and development of children of early and preschool age / Ed. L.A. Paramonova.

findings
1) "cementing" the basis of the content of preschool education in terms of its variability are 4 directions, corresponding to the main lines of child development: - cognitive speech;
- physical;
- social and personal;
- artistic and aesthetic.

findings

The recommended structure of the PLO preschool educational institutions
Mandatory part Programs
The second part (variable)Programs formed by participants of the educational process
Applications to the program.

Analysis of existing (integrated) programs
The program of education and training in kindergarten/ Ed. M.A. Vasilyeva, V.V. Gerbovoy, TS Komarova (2005 version).
Rainbow: Program of upbringing, education and development of preschool children in kindergarten conditions / Т.N. Doronova, S.G. Jacobson, E.V. Solovyov and others; Scientific hands T.N. Doronova.
Childhood: Program of development and education of children in kindergarten / V.I. Loginova, T.I. Babaeva, N.A. Notkina et al .; Ed. T.I. Babaeva, Z.A. Mikhailova, L.M. Gurovich,
The approximate educational program of education, training and development of children of early and preschool age / Ed. L.A. Paramonova.

findings
1) "cementing" the basis of the content of preschool education in terms of its variability are 4 directions, corresponding to the main lines of child development: - cognitive speech;
- physical;
- social and personal;
- artistic and aesthetic.

findings
The program of education and training in kindergarten/ Ed. M.A. Vasilyeva, V.V. Gerbovoy, TS Komarova (2005 version).
Rainbow: Program of upbringing, education and development of preschool children in kindergarten conditions / Т.N. Doronova, S.G. Jacobson, E.V. Solovyov and others; Scientific hands T.N. Doronova.
Childhood: Program of development and education of children in kindergarten / V.I. Loginova, T.I. Babaeva, N.A. Notkina et al .; Ed. T.I. Babaeva, Z.A. Mikhailova, L.M. Gurovich,
The approximate educational program of education, training and development of children of early and preschool age / Ed. L.A. Paramonova.
- cognitive speech;
- physical;
- social and personal;
- artistic and aesthetic.

findings
2) “fullness” of each of the above areas in the analyzed programs is heterogeneous in quantitative and qualitative terms;
3) at present there is no single point of view on what the content of pre-school education should be in order to ensure the achievement of a graduate kindergarten the level of physical and psychological readiness for school for the successful development of the basic general education programs of primary general education; 
4) the volume of educational load on the main areas of child development in existing programs is distributed quite unequally: 1st place - cognitive speech development (from 40 to 47% of classes);
2nd place - artistic and aesthetic development (from 20 to 40%);
3rd place - physical development (19-20%).
4th place - social and personal development (from 0 to 13%).

findings
1st place - cognitive speech development (from 40 to 47% of classes);
2nd place - artistic and aesthetic development (from 20 to 40%);
3rd place - physical development (19-20%).
4th place - social and personal development (from 0 to 13%).
5) in the framework of the above-mentioned main areas (social and personal, physical, cognitive, speech, artistic and aesthetic) the volume of educational load on various types of children's activities (playing, speaking, productive, etc.) is also represented unequally, in violation of the principles of age approach to education of preschool children and the requirements of SanPiN. 
"Integration of the content of preschool education" –
the state (or process leading to such a state) of connectedness, interpenetration and interaction of individual educational areas of the content of pre-school education, ensuring the integrity of the educational process.

Recommendations for the development of the content sections of the PLO

“Mandatory part of the basic general educational program of preschool education”–
the state (or process leading to such a state) of connectedness, interpenetration and interaction of individual educational areas of the content of pre-school education, ensuring the integrity of the educational process.

Recommendations for the development of the content sections of the PLO

“Mandatory part of the basic general educational program of preschool education”–

Recommendations for the development of the content sections of the PLO

“Mandatory part of the basic general educational program of preschool education”–
part of the basic general education program, which must be implemented in any educational institution (group) that implements the basic general educational program of pre-school education. Provides achievement pupils readiness for school.In compensating and combined orientation groups, it includes activities on the qualified correction of deficiencies in the physical and (or) mental development of children with disabilities.

explanatory note;
the organization of the mode of stay of children in an educational institution;
the content of psychological and pedagogical work on the development of children's educational areas "Physical Education", "Health", "Security", "Socialization," Labor "," Cognition "," Communication "," Reading fiction "," Fiction "," Music";

The mandatory part of the Program should contain the following sections:
content of remedial work (for children with disabilities);
the planned results of the mastering by children of the basic general educational program of pre-school education;
system for monitoring the achievement of the planned results of the Program implementation by children.

The second part of the Program, formed by the participants of the educational process, should reflect:
1) species diversity of institutions
the presence of priority activities, including to ensure equal starting opportunities for teaching children in general education institutions,
"Part of the main general educational program of preschool education, formed by the participants of the educational process" –
this is part of the main general educational program of preschool education, formed by the participants of the educational process in addition to the mandatory part, and reflecting: 1) the species diversity of institutions (groups), the presence of priority activities (except for activities on the qualified correction of deficiencies in the physical and (or) mental development of children with limited health); 2) the specifics of the socio-economic, national-cultural, demographic, climatic and other conditions in which the educational process takes place.

Each preschool educational institution has its own individual, peculiar only to it means of realizing its mission.
That is what they need to designate.

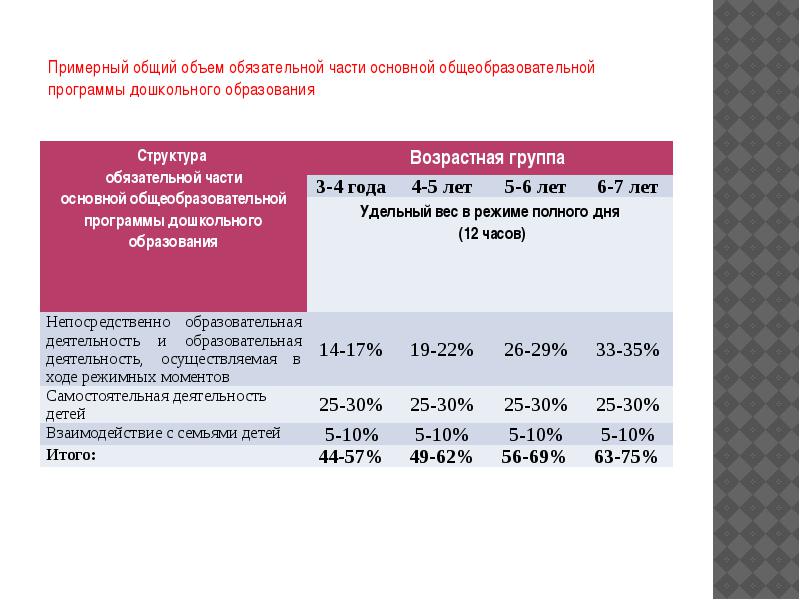
The total amount of the mandatory part of the basic general education program, which should be implemented in any educational institution (group), except for compensating and combined orientation groups,
calculated in accordance with the age of pupils, the main directions of their development, the specifics of pre-school education and includes the time allotted for: directly educational activities;
educational activities carried out during regime moments;
interaction with families of children in the implementation of the basic general education program of preschool education

Approximate total amount of the mandatory part of the basic general education program of preschool education
The volume of the mandatory part of the basic general educational program of preschool education does not include the time allotted for: joint activities of an adult and children, carried out during regime moments, and aimed at exercising the functions of supervision and / or care;
daytime sleep (in groups of full, abbreviated, extended days and twenty-four-hour stay).

directly educational activities;
educational activities carried out during regime moments;
interaction with families of children in the implementation of the basic general education program of preschool education
joint activities of an adult and children, carried out during regime moments, and aimed at exercising the functions of supervision and / or care;
daytime sleep (in groups of full, abbreviated, extended days and twenty-four-hour stay).
The optimal share is the equal share of the volumes of the mandatory part of the basic general educational program of preschool education in the main areas of children's development, such as physical, social and personal, cognitive-verbal, artistic and aesthetic (approximately 25% of the total). 
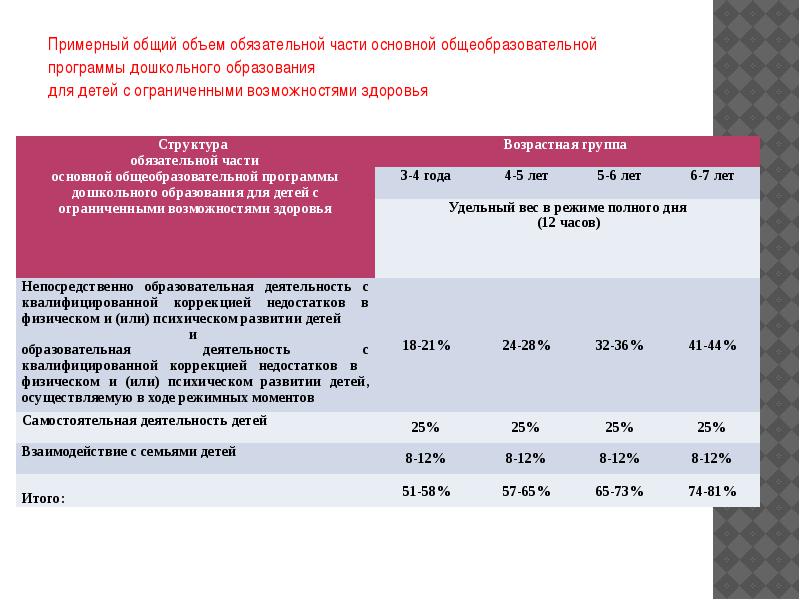
The total amount of the mandatory part of the basic general education program for children with disabilities, which should be implemented in groups of compensating and combined orientation,
includes the time allotted for: directly educational activities with qualified correction of deficiencies in the physical and (or) mental development of children;
educational activities with qualified correction of deficiencies in the physical and (or) mental development of children, carried out during regime moments;
independent activities of children;
interaction with the families of children in the implementation of the basic general educational program of preschool education for children with disabilities

Approximate total amount of the compulsory part of the basic general educational program of preschool education for children with disabilities
an additional 5-6% to the directly educational activities of children and educational activities carried out during high-profile moments, the mandatory part of the basic general education program, if the institution, according to the results of state accreditation, has one priority area of activity;
additionally 11-12%, if the institution according to the results of state accreditation has two priority activities;

The approximate total volume of the part formed by the participants of the educational process
additionally 17-18%, if the institution has three priority activities according to the results of state accreditation;
additionally 24-25%, if the institution according to the results of state accreditation has all the priority activities.

"Joint activities of adults and children" -
directly educational activities with qualified correction of deficiencies in the physical and (or) mental development of children;
educational activities with qualified correction of deficiencies in the physical and (or) mental development of children, carried out during regime moments;
independent activities of children;
interaction with the families of children in the implementation of the basic general educational program of preschool education for children with disabilities
an additional 5-6% to the directly educational activities of children and educational activities carried out during high-profile moments, the mandatory part of the basic general education program, if the institution, according to the results of state accreditation, has one priority area of activity;
additionally 11-12%, if the institution according to the results of state accreditation has two priority activities;

The approximate total volume of the part formed by the participants of the educational process
additionally 17-18%, if the institution has three priority activities according to the results of state accreditation;
additionally 24-25%, if the institution according to the results of state accreditation has all the priority activities.

"Joint activities of adults and children" -
additionally 17-18%, if the institution has three priority activities according to the results of state accreditation;
additionally 24-25%, if the institution according to the results of state accreditation has all the priority activities.

"Joint activities of adults and children" -
the activity of two or more participants in the educational process (adults and pupils) to solve educational problems in the same space and at the same time. It is distinguished by the presence of a partner (equal) position of an adult and a partner form of organization (the possibility of free placement, movement and communication of children in the process of educational activities). Involves individual, subgroup and group forms of organization of work with pupils. 
"Independent activity of children" -
1) free activity of pupils in the conditions of the subject-developing educational environment created by the teachers, ensuring that each child chooses an activity according to his interests and allows him to interact with his peers or act individually;
2) organized by the tutor activities of students, aimed at solving problems related to the interests of other people (emotional well-being of other people, helping others in everyday life, etc.).

The main general educational program of preschool education
must: To ensure the protection and promotion of children's health, their comprehensive (physical, cognitive, speech, artistic and aesthetic, social and personal) development through the organization of various types of children's activities and amateur activities, of which play is the leading one.

To contribute to the achievement of a child’s level of development that ensures his psychological and physical readiness for school, to create equal conditions for the upbringing, development and training of children, regardless of the material wealth of the family, place of residence, language and cultural environment, ethnicity.
Comply with the principle of developmental education, the purpose of which is the development of the child.

Comply with the criteria of completeness, necessity and sufficiency (to allow to solve the goals and tasks set only on the necessary and sufficient material, as close as possible to a reasonable "minimum").
To form such qualities, knowledge and skills that are directly related to the development of children of preschool age.

Based on the complex thematic principle of the educational process. Program topics should be accessible to children and cause a positive emotional attitude, which is necessary for their respective motivation in the educational process.
To build on age-appropriate forms of work with children in the form of games, conversations, reading, observations, etc. The main form of work with children of preschool age is a game, which in the educational process is set by an adult.

Explanatory note

The purpose and objectives of the educational process
Purpose:
- creation of an integrated system for physical education and health of children. Tasks:
To ensure the protection and promotion of children's health, their comprehensive (physical, cognitive, speech, artistic and aesthetic, social and personal) development through the organization of various types of children's activities and amateur activities, of which play is the leading one.

To contribute to the achievement of a child’s level of development that ensures his psychological and physical readiness for school, to create equal conditions for the upbringing, development and training of children, regardless of the material wealth of the family, place of residence, language and cultural environment, ethnicity.
Comply with the principle of developmental education, the purpose of which is the development of the child.

Comply with the criteria of completeness, necessity and sufficiency (to allow to solve the goals and tasks set only on the necessary and sufficient material, as close as possible to a reasonable "minimum").
To form such qualities, knowledge and skills that are directly related to the development of children of preschool age.

Based on the complex thematic principle of the educational process. Program topics should be accessible to children and cause a positive emotional attitude, which is necessary for their respective motivation in the educational process.
To build on age-appropriate forms of work with children in the form of games, conversations, reading, observations, etc. The main form of work with children of preschool age is a game, which in the educational process is set by an adult.

Explanatory note

The purpose and objectives of the educational process
Purpose:
- creation of an integrated system for physical education and health of children. Tasks:
To ensure the protection and promotion of children's health, their comprehensive (physical, cognitive, speech, artistic and aesthetic, social and personal) development through the organization of various types of children's activities and amateur activities, of which play is the leading one.

To contribute to the achievement of a child’s level of development that ensures his psychological and physical readiness for school, to create equal conditions for the upbringing, development and training of children, regardless of the material wealth of the family, place of residence, language and cultural environment, ethnicity.
Comply with the principle of developmental education, the purpose of which is the development of the child.

Comply with the criteria of completeness, necessity and sufficiency (to allow to solve the goals and tasks set only on the necessary and sufficient material, as close as possible to a reasonable "minimum").
To form such qualities, knowledge and skills that are directly related to the development of children of preschool age.

Based on the complex thematic principle of the educational process. Program topics should be accessible to children and cause a positive emotional attitude, which is necessary for their respective motivation in the educational process.
To build on age-appropriate forms of work with children in the form of games, conversations, reading, observations, etc. The main form of work with children of preschool age is a game, which in the educational process is set by an adult.

Explanatory note

The purpose and objectives of the educational process
Purpose:
- creation of an integrated system for physical education and health of children. Tasks:

Comply with the criteria of completeness, necessity and sufficiency (to allow to solve the goals and tasks set only on the necessary and sufficient material, as close as possible to a reasonable "minimum").
To form such qualities, knowledge and skills that are directly related to the development of children of preschool age.

Based on the complex thematic principle of the educational process. Program topics should be accessible to children and cause a positive emotional attitude, which is necessary for their respective motivation in the educational process.
To build on age-appropriate forms of work with children in the form of games, conversations, reading, observations, etc. The main form of work with children of preschool age is a game, which in the educational process is set by an adult.

Explanatory note

The purpose and objectives of the educational process
Purpose:
- creation of an integrated system for physical education and health of children. Tasks:

The purpose and objectives of the educational process
Purpose:
- creation of an integrated system for physical education and health of children. Tasks:
Tasks:
Provide a rational organization of children's motor activity; - to create conditions for children's health regimes; - to increase attention to the formation of correct posture; - to promote the formation of a healthy lifestyle for children in constant interaction with the family. 
1. Comprehensive preschool education program "Rainbow"(bibliographic description of the document according to GOST).
2. Partial programs:
- “Our home is nature” (N. Ryzhova); - “Start” (L. Yakovlev, R. Rodin) and others. Partial programs should be selected to “strengthen” any least developed sections of the integrated program.

3. The correctional program for special (correctional) educational institutions of the 4th type (for children with visual impairment), ed. L.I. Plaksinoy.

4. Scientific and methodological materials substantiating the content of correctional work in kindergarten, for example:
- A.V. Grishvina, E.Ya. Puzyrevskaya, E.V. Sochevanov. "Games-activities with young children with impaired mental and speech development"; - N.D. Shmatko. "Children with developmental disabilities", etc.

1. Organization of the regime of stay of children in an educational institution

Flexible mode of activity depending on the social order of parents, the availability of specialists, teachers, medical workers, approaches to the development and upbringing of preschoolers, to the organization of all types of children's activities

Graphs of interaction of teachers, specialists and educators;
Model of the educational process using a variety of forms and taking into account the time of year and the age-related psycho-physiological capabilities of children, the relationship of planned activities with the daily life of children in kindergarten

- The system of tempering activities;
- The system of sports and recreational activities

2. The content of psychological and pedagogical work on the development of children's educational areas

3. Content of remedial work (for children with disabilities

includes activities to correct deficiencies in the physical and / or mental development of children with disabilities.
This section also includes a selection of programs and technologies used in pre-school in accordance with the direction of correction

4. The planned results of the development of children of the basic general educational program of preschool education.

Interim Assessment
(once every six months or once a year) is a description of the dynamics of the formation of the integrative qualities of the pupils of each age group for mastering the Program in all areas of children's development;
- these are monitoring results

final grade
carried out with the release of a child from kindergarten to school and includes a description of the integrative qualities of a graduate of DOU.
Held annually in the preparatory school group.
A portrait of a graduate can be compiled by the DOE teaching staff, taking into account regulatory documents

5. The monitoring system of the achievement by children of the planned results of the Program implementation

System of monitoring the achievement of children planned results of the program should provide an integrated assessment approach totals and intermediate the results of the implementation of the Program, allow the assessment of the dynamics of children's achievements and include description of the object, forms, frequency and contentmonitoring.

The monitoring process examines physical, intellectual and personal qualities.

Time is planned to conduct psychological and pedagogical diagnostics of the results of the Program: 5-7 days in September and May.


Features of the organization of the educational process
The section describes the features of the organization of the educational process in a preschool educational institution, which ensure the achievement of the planned results of joint activities, for example:

In the mode of preschool educational institutions; - in the leading forms of conducting classes; - in the organization of the subject-developing environment; - in the selection of personnel; - in features of the organization and holding of various events; - in establishing a social partnership; - in collaboration with the family; - in the tradition of pre-school educational institutions, etc.

It is desirable to highlight those features of the educational and educational process of the kindergarten that distinguish it from other pre-school educational institutions.
For example, organizing the work of groups separately for boys and girls; short stay, etc.

It is also recommended to mention the additional educational services provided by the institution both within the framework of budget financing and on a fee-based basis, which reinforce the priority activity chosen by the kindergarten.

Appendices to OOP
- the composition of the working group on the development of EP; - work plan of the working group; - expert opinion on the OP; - the protocol of the pedagogical council on the approval of the EP; - order for preschool educational institutions on the implementation of the EP, indicating those responsible for certain areas; - Plan for the implementation of the educational program of pre-school; - diagnostic methods (“instrument”) to section 6;

Appendices to OOP
Glossary of key terms used by members of the teaching staff within an educational institution; - results of diagnostics of the implementation of the educational program; - analytical materials justifying the content of sections of the educational program; - analytical materials, justifying the need for changes and additions to the sections of the educational program.

Kornilova Marina Vladimirovna,

3. The correctional program for special (correctional) educational institutions of the 4th type (for children with visual impairment), ed. L.I. Plaksinoy.

4. Scientific and methodological materials substantiating the content of correctional work in kindergarten, for example:
- A.V. Grishvina, E.Ya. Puzyrevskaya, E.V. Sochevanov. "Games-activities with young children with impaired mental and speech development"; - N.D. Shmatko. "Children with developmental disabilities", etc.

1. Organization of the regime of stay of children in an educational institution

Flexible mode of activity depending on the social order of parents, the availability of specialists, teachers, medical workers, approaches to the development and upbringing of preschoolers, to the organization of all types of children's activities

Graphs of interaction of teachers, specialists and educators;
Model of the educational process using a variety of forms and taking into account the time of year and the age-related psycho-physiological capabilities of children, the relationship of planned activities with the daily life of children in kindergarten

- The system of tempering activities;
- The system of sports and recreational activities

2. The content of psychological and pedagogical work on the development of children's educational areas


3. Content of remedial work (for children with disabilities

includes activities to correct deficiencies in the physical and / or mental development of children with disabilities.
This section also includes a selection of programs and technologies used in pre-school in accordance with the direction of correction

4. The planned results of the development of children of the basic general educational program of preschool education.

Interim Assessment
(once every six months or once a year) is a description of the dynamics of the formation of the integrative qualities of the pupils of each age group for mastering the Program in all areas of children's development;
- these are monitoring results

final grade
carried out with the release of a child from kindergarten to school and includes a description of the integrative qualities of a graduate of DOU.
Held annually in the preparatory school group.
A portrait of a graduate can be compiled by the DOE teaching staff, taking into account regulatory documents

5. The monitoring system of the achievement by children of the planned results of the Program implementation

System of monitoring the achievement of children planned results of the program should provide an integrated assessment approach totals and intermediate the results of the implementation of the Program, allow the assessment of the dynamics of children's achievements and include description of the object, forms, frequency and contentmonitoring.

The monitoring process examines physical, intellectual and personal qualities.

Time is planned to conduct psychological and pedagogical diagnostics of the results of the Program: 5-7 days in September and May.


Features of the organization of the educational process
The section describes the features of the organization of the educational process in a preschool educational institution, which ensure the achievement of the planned results of joint activities, for example:

In the mode of preschool educational institutions; - in the leading forms of conducting classes; - in the organization of the subject-developing environment; - in the selection of personnel; - in features of the organization and holding of various events; - in establishing a social partnership; - in collaboration with the family; - in the tradition of pre-school educational institutions, etc.

It is desirable to highlight those features of the educational and educational process of the kindergarten that distinguish it from other pre-school educational institutions.
For example, organizing the work of groups separately for boys and girls; short stay, etc.

It is also recommended to mention the additional educational services provided by the institution both within the framework of budget financing and on a fee-based basis, which reinforce the priority activity chosen by the kindergarten.


Appendices to OOP
- the composition of the working group on the development of EP; - work plan of the working group; - expert opinion on the OP; - the protocol of the pedagogical council on the approval of the EP; - order for preschool educational institutions on the implementation of the EP, indicating those responsible for certain areas; - Plan for the implementation of the educational program of pre-school; - diagnostic methods (“instrument”) to section 6;

Appendices to OOP
Glossary of key terms used by members of the teaching staff within an educational institution; - results of diagnostics of the implementation of the educational program; - analytical materials justifying the content of sections of the educational program; - analytical materials, justifying the need for changes and additions to the sections of the educational program.

Kornilova Marina Vladimirovna,

Flexible mode of activity depending on the social order of parents, the availability of specialists, teachers, medical workers, approaches to the development and upbringing of preschoolers, to the organization of all types of children's activities

Graphs of interaction of teachers, specialists and educators;
Model of the educational process using a variety of forms and taking into account the time of year and the age-related psycho-physiological capabilities of children, the relationship of planned activities with the daily life of children in kindergarten

- The system of tempering activities;
- The system of sports and recreational activities

2. The content of psychological and pedagogical work on the development of children's educational areas


3. Content of remedial work (for children with disabilities

includes activities to correct deficiencies in the physical and / or mental development of children with disabilities.
This section also includes a selection of programs and technologies used in pre-school in accordance with the direction of correction

4. The planned results of the development of children of the basic general educational program of preschool education.

Interim Assessment
(once every six months or once a year) is a description of the dynamics of the formation of the integrative qualities of the pupils of each age group for mastering the Program in all areas of children's development;
- these are monitoring results

final grade
carried out with the release of a child from kindergarten to school and includes a description of the integrative qualities of a graduate of DOU.
Held annually in the preparatory school group.
A portrait of a graduate can be compiled by the DOE teaching staff, taking into account regulatory documents

5. The monitoring system of the achievement by children of the planned results of the Program implementation

System of monitoring the achievement of children planned results of the program should provide an integrated assessment approach totals and intermediate the results of the implementation of the Program, allow the assessment of the dynamics of children's achievements and include description of the object, forms, frequency and contentmonitoring.

The monitoring process examines physical, intellectual and personal qualities.

Time is planned to conduct psychological and pedagogical diagnostics of the results of the Program: 5-7 days in September and May.


Features of the organization of the educational process
The section describes the features of the organization of the educational process in a preschool educational institution, which ensure the achievement of the planned results of joint activities, for example:

In the mode of preschool educational institutions; - in the leading forms of conducting classes; - in the organization of the subject-developing environment; - in the selection of personnel; - in features of the organization and holding of various events; - in establishing a social partnership; - in collaboration with the family; - in the tradition of pre-school educational institutions, etc.

It is desirable to highlight those features of the educational and educational process of the kindergarten that distinguish it from other pre-school educational institutions.
For example, organizing the work of groups separately for boys and girls; short stay, etc.

It is also recommended to mention the additional educational services provided by the institution both within the framework of budget financing and on a fee-based basis, which reinforce the priority activity chosen by the kindergarten.


Appendices to OOP
- the composition of the working group on the development of EP; - work plan of the working group; - expert opinion on the OP; - the protocol of the pedagogical council on the approval of the EP; - order for preschool educational institutions on the implementation of the EP, indicating those responsible for certain areas; - Plan for the implementation of the educational program of pre-school; - diagnostic methods (“instrument”) to section 6;

Appendices to OOP
Glossary of key terms used by members of the teaching staff within an educational institution; - results of diagnostics of the implementation of the educational program; - analytical materials justifying the content of sections of the educational program; - analytical materials, justifying the need for changes and additions to the sections of the educational program.

Kornilova Marina Vladimirovna,

includes activities to correct deficiencies in the physical and / or mental development of children with disabilities.
This section also includes a selection of programs and technologies used in pre-school in accordance with the direction of correction

4. The planned results of the development of children of the basic general educational program of preschool education.

Interim Assessment
(once every six months or once a year) is a description of the dynamics of the formation of the integrative qualities of the pupils of each age group for mastering the Program in all areas of children's development;
- these are monitoring results

final grade
carried out with the release of a child from kindergarten to school and includes a description of the integrative qualities of a graduate of DOU.
Held annually in the preparatory school group.
A portrait of a graduate can be compiled by the DOE teaching staff, taking into account regulatory documents

5. The monitoring system of the achievement by children of the planned results of the Program implementation

System of monitoring the achievement of children planned results of the program should provide an integrated assessment approach totals and intermediate the results of the implementation of the Program, allow the assessment of the dynamics of children's achievements and include description of the object, forms, frequency and contentmonitoring.

The monitoring process examines physical, intellectual and personal qualities.

Time is planned to conduct psychological and pedagogical diagnostics of the results of the Program: 5-7 days in September and May.


Features of the organization of the educational process
The section describes the features of the organization of the educational process in a preschool educational institution, which ensure the achievement of the planned results of joint activities, for example:

In the mode of preschool educational institutions; - in the leading forms of conducting classes; - in the organization of the subject-developing environment; - in the selection of personnel; - in features of the organization and holding of various events; - in establishing a social partnership; - in collaboration with the family; - in the tradition of pre-school educational institutions, etc.

It is desirable to highlight those features of the educational and educational process of the kindergarten that distinguish it from other pre-school educational institutions.
For example, organizing the work of groups separately for boys and girls; short stay, etc.

It is also recommended to mention the additional educational services provided by the institution both within the framework of budget financing and on a fee-based basis, which reinforce the priority activity chosen by the kindergarten.


Appendices to OOP
- the composition of the working group on the development of EP; - work plan of the working group; - expert opinion on the OP; - the protocol of the pedagogical council on the approval of the EP; - order for preschool educational institutions on the implementation of the EP, indicating those responsible for certain areas; - Plan for the implementation of the educational program of pre-school; - diagnostic methods (“instrument”) to section 6;

Appendices to OOP
Glossary of key terms used by members of the teaching staff within an educational institution; - results of diagnostics of the implementation of the educational program; - analytical materials justifying the content of sections of the educational program; - analytical materials, justifying the need for changes and additions to the sections of the educational program.

Kornilova Marina Vladimirovna,
(once every six months or once a year) is a description of the dynamics of the formation of the integrative qualities of the pupils of each age group for mastering the Program in all areas of children's development;
- these are monitoring results
carried out with the release of a child from kindergarten to school and includes a description of the integrative qualities of a graduate of DOU.
Held annually in the preparatory school group.
A portrait of a graduate can be compiled by the DOE teaching staff, taking into account regulatory documents

System of monitoring the achievement of children planned results of the program should provide an integrated assessment approach totals and intermediate the results of the implementation of the Program, allow the assessment of the dynamics of children's achievements and include description of the object, forms, frequency and contentmonitoring.

The monitoring process examines physical, intellectual and personal qualities.

Time is planned to conduct psychological and pedagogical diagnostics of the results of the Program: 5-7 days in September and May.


Features of the organization of the educational process
The section describes the features of the organization of the educational process in a preschool educational institution, which ensure the achievement of the planned results of joint activities, for example:

In the mode of preschool educational institutions; - in the leading forms of conducting classes; - in the organization of the subject-developing environment; - in the selection of personnel; - in features of the organization and holding of various events; - in establishing a social partnership; - in collaboration with the family; - in the tradition of pre-school educational institutions, etc.

It is desirable to highlight those features of the educational and educational process of the kindergarten that distinguish it from other pre-school educational institutions.
For example, organizing the work of groups separately for boys and girls; short stay, etc.

It is also recommended to mention the additional educational services provided by the institution both within the framework of budget financing and on a fee-based basis, which reinforce the priority activity chosen by the kindergarten.


Appendices to OOP
- the composition of the working group on the development of EP; - work plan of the working group; - expert opinion on the OP; - the protocol of the pedagogical council on the approval of the EP; - order for preschool educational institutions on the implementation of the EP, indicating those responsible for certain areas; - Plan for the implementation of the educational program of pre-school; - diagnostic methods (“instrument”) to section 6;

Appendices to OOP
Glossary of key terms used by members of the teaching staff within an educational institution; - results of diagnostics of the implementation of the educational program; - analytical materials justifying the content of sections of the educational program; - analytical materials, justifying the need for changes and additions to the sections of the educational program.

Kornilova Marina Vladimirovna,
Time is planned to conduct psychological and pedagogical diagnostics of the results of the Program: 5-7 days in September and May.


Features of the organization of the educational process
The section describes the features of the organization of the educational process in a preschool educational institution, which ensure the achievement of the planned results of joint activities, for example:

In the mode of preschool educational institutions; - in the leading forms of conducting classes; - in the organization of the subject-developing environment; - in the selection of personnel; - in features of the organization and holding of various events; - in establishing a social partnership; - in collaboration with the family; - in the tradition of pre-school educational institutions, etc.

It is desirable to highlight those features of the educational and educational process of the kindergarten that distinguish it from other pre-school educational institutions.
For example, organizing the work of groups separately for boys and girls; short stay, etc.

It is also recommended to mention the additional educational services provided by the institution both within the framework of budget financing and on a fee-based basis, which reinforce the priority activity chosen by the kindergarten.


Appendices to OOP
- the composition of the working group on the development of EP; - work plan of the working group; - expert opinion on the OP; - the protocol of the pedagogical council on the approval of the EP; - order for preschool educational institutions on the implementation of the EP, indicating those responsible for certain areas; - Plan for the implementation of the educational program of pre-school; - diagnostic methods (“instrument”) to section 6;

Appendices to OOP
Glossary of key terms used by members of the teaching staff within an educational institution; - results of diagnostics of the implementation of the educational program; - analytical materials justifying the content of sections of the educational program; - analytical materials, justifying the need for changes and additions to the sections of the educational program.

Kornilova Marina Vladimirovna,
Municipal institution
"Education Department of the City of Biysk"
Information and Methodological Center
Development of the educational program
preschool educational institution.
Biysk
Compiled by:
– methodist IMC MU "Education Management of the City of Biysk"
– head of Municipal Educational Institution "Kindergarten № 51"
The development of the educational program of preschool educational institutions. Guidelines.
The educational program of a pre-school educational institution is developed in accordance with the requirements of the main regulatory documents: Russian Federation “On Education” and the Model Provision on a pre-school educational institution is a mandatory regulatory document developed and implemented by each educational institution independently. Paragraph 21 of the Model Provision on a pre-school educational institution states that “the content of the educational process in a pre-school educational institution is determined by the educational program of pre-school education developed, adopted and implemented by it independently.”
The educational program of a pre-school educational institution is one of the main regulatory documents governing its livelihoods. Along with the Charter, it serves as the basis for licensing, accreditation, changes in budget financing, organization of paid educational services in accordance with the social order of parents (legal representatives).
Along with the Charter of an educational institution, a license for the right to conduct educational activities, a certificate of state accreditation of an educational institution, it is necessary to acquaint parents with documents regulating the organization of the educational process, individually conclude a parental agreement. Among the other documents with which it is necessary to acquaint parents, first of all, it is necessary to note the educational program of preschool education. This document will guide parents to information about the educational services provided, which in turn will help to ensure the realization of parents' right to choose educational services, the right to guarantee their receipt.
The practitioners are currently hampered in developing a high-quality educational program by the discrepancies in the definition of the very concept of “educational program”, which various authors interpret either as a development program or as a program reflecting the specifics of an institution’s educational activities or as a document allowing individualization of pupils' educational routes. The most common misconception is that an educational program is often identified with a curriculum implemented in a particular pre-school institution. At the same time, there is a real experience in developing educational programs by analogy with the school model or on the basis of the own logic of understanding this document. Thus, it is possible to fix one more obvious contradiction between the requirement of the Law of the Russian Federation “On Education” and other regulatory documents on the development and implementation of each educational institution independently. ”
The practical significance of this issue, its relevance determined the logic of the selection of materials for this manual. The presented materials reflect the main goals and specifics of the preschool educational institution, the program of which should be structured taking into account the peculiarities of the organization of work with children of preschool age, when the values of development and education prevail.
In accordance with the approval and implementation of the Federal State requirements for the structure of the main general educational program of pre-school education (Order of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation No. 000 of 01/01/01), the form and structure change Educational program DOW.
Currently, on the basis of federal requirements, the following are being developed:
the approximate basic educational program of preschool education;
approximate basic educational program of preschool education for children with disabilities.
Prior to the implementation of these two programs, these recommendations are temporary.
General provisions
The concept of "educational program" entered the teaching practice after the adoption of the Law of the Russian Federation "On Education".
Educational program - regulatory document, justifying the choice of goals, content, applied methods and technologies, forms of organization of the educational process in each specific pre-school educational institution (S. Kuzmin).
Educational program - This is a specific model of the educational process of a preschool institution. It should cover all types of children's activities (and not just education), taking into account their priority in each age period ().
DOW educational program - it is a complex of a certain educational content, certain means of pedagogical communication (forms, methods and means of training and education), as well as personnel and material conditions for the realization of the educational needs of pupils ().
Educational program - a document defining the specifics of the organization of the educational process (content, form), taking into account the standard of preschool education. This is a model of the educational process. It sets out the multi-component content of education and consists of a whole series of parts interconnected. The selection of components cannot be random and should be focused primarily on the creation of a complete system ().
Educational program - This is a document that is subject to constant (annual) adjustment.
The purpose of the educational program is determined based on the fact that it is an internal (for a given institution) educational standard, determined by the municipal program for the development of education, the logic of the development of the educational institution itself, its capabilities, educational needs of the main social customers - parents (legal representatives).
The purpose of the educational program is a motivated substantiation of the content of the educational process, the choice of a general education program in each specific pre-school educational institution.
Summarizing all the above, a preschool educational program can be defined as: normative document, internal standard of the institution, determining the content of pre-school education, developed in the main areas of children's development and representing a set of tools for the upbringing, education, rehabilitation, development and correction of children, implemented on the basis of available resources (human and material) in accordance with the social order of the territory.
The educational program should cover all the main moments of children's life, and not just education, taking into account the priority of children's activities in each age period.
The program should show:
· How, taking into account the specific conditions and characteristics of a contingent of pupils in any type of preschool educational institution, its own unconventional model of organizing education, education and development of preschool children is created;
· What new pedagogical technologies are used in working with children;
· How are the individual characteristics and capabilities of the pupils taken into account.
The educational program of preschool educational institutions should not be considered as a document once written and not subject to correction. The structure and content of the educational program is determined, as a rule, for a period of 3-5 years, but if necessary, teachers adjust them in accordance with actual conditions annually.
The structure of the educational program of preschool educational institutions
Since at present there are different points of view on the essence of the educational program and different approaches to determining its content, we propose to consider the “model” of the structure of the educational program of a preschool educational institution as exemplary.
Title page.
When and by whom it was approved, where it was reviewed, with whom the program was agreed upon. The name of the program with the full name of the institution.
Name of settlement, year of development.
Section 1. General Provisions.
1.1. Explanatory note.
1.2. Information reference about DOW.
2.1. Analysis of the material and technical base of preschool educational institutions.
2.2. Analysis of the main achievements and problems of teachers.
2.3. Analysis of the medical and social conditions of children in preschool.
2.4. Analysis of the results of the educational process.
2.5. Analysis of personality-oriented interaction with parents of pupils and social institutions.
2.6. Characteristics of the social order for education.
educational institution.
Section 6. The content of the educational process.
6.1. Implemented programs of preschool education, their justification
6.2. Characteristics of the main didactic and methodological manuals, focused on the main directions of development of children.
Section 7. Design and Pedagogical Planning
activities, building a holistic teaching
process.
7.1. Principles of the organization of the educational process.
7.2. The system for the implementation of the preschool educational program
education.
7.3. Regimes of the day for the cold and warm period by age groups,
according to the implemented general education program
preschool education.
7.4. The system of work on the adaptation of new arrivals to the conditions of preschool educational institutions.
7.6. Syllabus.
7.7. Timetable of classes.
7.8. Schedule work circles.
7.9. Correction and interaction of specialists in providing
individual support pupils.
7.10. Planning the content of the educational process for the month in the morning and evening hours.
7.11. The system of sports and recreational work.
7.12. Catering.
7.13. Planning a system of holidays and entertainment.
7.14. Educational system DOW.
Section 8. Monitoring the development of children.
Section 9. Conditions for the implementation of the pre-school educational program.
9.1. Regulatory framework for the implementation of the program.
9.2. Dow control system.
9.3. Model methodical work.
9.4. The model of interaction of preschool specialists.
9.5. Forms of work with parents.
9.6. Continuity in the work of pre-school and school.
9.7. Dow interaction with other institutions.
9.8. Subject-spatial organization of DOU.
9.9. Dynamics of professional growth and individual achievements of teachers.
9.10. Plan card innovation work DOW. Innovative projects of teachers.
The educational program contains a variety of information about the features of the activities of the preschool institution as a whole by age groups. The quality of the educational activity of an institution depends on how competently and systemically this information is presented in the program.
1. Title page.
On the title page of the educational program it is advisable to provide the following information:
· In the upper left corner of the sheet there is information about where the program was reviewed and adopted (for example, adopted at the DOE Council, protocol No. ___ dated _______);
· In the upper right corner there is information about the approval of the program (for example, I Approve. The head of the kindergarten "Kindergarten No. ___". The signature of the head of the institution, the transcript and the seal;
· In the central part of the title page, the full name of the institution is given (for example, the “Educational program of the kindergarten“ Kindergarten No. __ ”of the combined type, category II);
· The names of authors, developers of the program (teachers of the group, as well as the head, senior educator, psychologist, speech therapist, educator) or creative team, including also specialists from other educational institutions (supervisor, education management specialist) ;
· In the lower part of the title page, the name of the settlement in which the pre-school and the year of the development of the educational program are located are indicated.
Section 1. General Provisions.
The section "General Provisions" includes an explanatory note and an information note about the DOE.
AT explanatory note It indicates the main conceptual approaches used in the development of the program, a description of its goals and values, and the expected timing of its implementation.
In the concept of the program, it is important to provide a justification of the relevance for the institution of the development of a program version. As a rule, when justifying the choice of an educational program option, the following actual positions are noted:
· The educational program takes into account the needs of the child contingent, which is especially important for institutions with priorities in activities (for example, children with developmental problems attend the DOE requiring specialized correction, therefore, the program provides for a system of correctional and developmental work with children),
· The content of education can be focused on the order of parents, which is important to take into account the DOE - Development Centers (in this regard, the program includes relevant content of additional education, or alternative services are organized for families of the microdistrict),
· When developing the program, cultural and educational features of the territory are also taken into account, which is important for pre-school institutions of any kind (in this case, the content includes the regional component of education, for example, regional programs and technologies for museum-pedagogical work, local history),
· When developing an educational program (EP), the peculiarities of the activities of pre-school educational institutions, their level of qualification can also be taken into account, allowing to expand the educational content implemented on the group at the expense of the methodological support developed by teachers.
The concept also includes a description of the objectives and values of the program. Values As a rule, they correspond to the general ideological orientations of education (the diversified development of a child, the upbringing of moral consciousness and behavior, a healthy lifestyle, the formation of a general culture of a person, etc.). Goals implemented by the educational program, they are a concrete definition of the goals of general education and can be different, but regardless of its specific option, they are aimed at the realization of the conditions for training, education, development and rehabilitation of pupils. The goals and objectives of the educational institution are also defined in accordance with the Model Provision on pre-school educational institution, its Charter and implemented programs and technologies.
AT information certificateabout preschool educational institution should be noted:
General information.
· Full name (with type, type) and address of the institution (legal address, actual address, phone, fax, e-mail).
· Head (FIO).
· Priority direction in educational activities.
· Brief historical background.
· Designed capacity and real capacity.
· Listing of premises and facilities of pre-school.
Founder MDOU.
Founding documents.
DOW structure (total number of groups, number of specialized groups, information about population size).
The personnel potential of preschool educational institutions: total employees - ..., from them administrative staff - ... people, teaching staff - ... people, educational support staff - ... people, attendants - ... people.
You must submit a social passport DOW.
You can provide information that reveals the personality of the DOW.
Section 2. Problem-oriented analysis of activities.
This section of the educational program includes a description of the social order for education, the main achievements and problems of teachers.
The analysis of the main achievements and problems is presented in the educational program, taking into account the implemented content in accordance with the diagnostic tools used by teachers.
In this section of the program, the generalized results of training, education, development, correction and health improvement of pupils are presented, usually in the form of summary tables or diagrams: for example,
· The level of social competence and education of children;
· Total number or% of children who have mastered the program (according to the levels represented in the comprehensive programs being implemented);
· The results of the development of children of different activities;
· The dynamics of the development of physical qualities of students;
· Incidence rates (for 3 years);
· The number or percentage of children released with clean speech;
· The number of children who have a readiness for school;
· Results of children's adaptation in primary school;
· Other results in accordance with the content held in pre-school diagnostics.
Section 3. Purpose of preschool educational institutions.
In this section, it is necessary to formulate the purpose of a specific pre-school educational institution. It is formulated in accordance with the Model Provision on a pre-school educational institution, based on the status, type (for which category of children), the state and municipal orders, and is justified by the possibilities of a particular educational institution and the needs of the family.
The formulation of the destination should be brief and understandable both to the teaching staff and to the closest social environment of the pre-school educational institution and first of all family.
Section 4. Description of the "model" of the preschool graduate
educational institution.
A graduate model is understood to be the intended result of the joint activities of the kindergarten and the family, which characterizes their ideas about the most important qualities personality of the child, which should have a graduate of a preschool educational institution. The graduate model is developed in accordance with the Federal State Requirements for the structure of the main general educational program of pre-school education, the chosen educational content (implemented by the main and partial general educational programs), the specifics and purpose of a specific pre-school educational institution.
Graduate model is of great importance. Firstly, it performs an integrative role in relation to other constituent images of a preschool institution, secondly, it is the basis for the development of targets for the educational process, allowing for maximum consideration for the environment, the specifics of the institution, the originality of the teaching staff. Thirdly, the graduate model serves as the main criterion of the effectiveness of the educational process, thanks to which it is possible to correlate the results obtained with the opinion of teachers, medical workers of pre-school and parents about the desired results.
1. It is useful to correlate the projected image of the graduate with the state educational standard, previous achievements of the teaching staff of this educational institution, the results of work educational institutions similar type and type.
2. It is necessary to include in the image of a graduate both qualitative and quantitative parameters of a pupil’s personal development.
3. The basic parameters of a graduate's preparedness should be stated on the basis of the priority of the functions of this educational institution, its purpose.
4. The image of a graduate is a minimum program that allows members of the pedagogical team to focus not only on the formation of common qualities, but also on the support and development of the child’s unique personality traits.
5. It is useful to design the image of a graduate of a particular pre-school educational institution, taking into account the opinions of the nearest educational institutions in which graduates will continue their education. This will help to strengthen the continuity ties in the upbringing and development of pupils at different levels of education.
The description of the graduate model can be based on the description of the integrative qualities of a preschooler child:
physically developedwho has mastered the basic cultural and hygienic skills. The child has formed the basic physical qualities and the need for physical activity. Independently performs the age-accessible hygienic procedures, complies with the elementary rules of a healthy lifestyle;
inquisitive, active. She is interested in the new, unknown in the surrounding world (the world of objects and things, the world of relationships and her inner world). Asks questions to adults, likes to experiment. Able to act independently (in everyday lifein various types of children's activities). In cases of difficulty appeals for help to an adult. Takes a lively, interested part in the educational process;
emotionally responsive. Responds to the emotions of loved ones and friends. Empathizes to characters of fairy tales, stories, stories. Emotionally reacts to works of art, music and art works, the natural world;
mastered the means of communication and ways to interact with adults and peers. The child adequately uses verbal and non-verbal means of communication, has a dialogical speech and constructive ways of interacting with children and adults (it agrees, exchanges objects, distributes actions in cooperation). Able to change the style of communication with an adult or a peer, depending on the situation;
able to control his behavior and plan their actions on the basis of primary value ideas, observing elementary generally accepted norms and rules of conduct. The behavior of the child is mainly determined not by short-term desires and needs, but by the demands of adults and the primary value notions of "what is good and what is bad." The child is able to plan their actions aimed at achieving a specific goal. Observes the rules of behavior on the street (road rules), in public places (transport, shop, clinic, theater, etc.);
able to solve intellectual and personal tasks (problems), adequate age. A child can apply independently learned knowledge and methods of activity to solve ready-made tasks (problems) set for both adults and themselves; depending on the situation, it can transform ways of solving problems (problems). The child is able to offer his own idea and translate it into a drawing, construction, story, etc .;
having primary ideas about yourself, family, society, state, world and nature. The child has an idea about himself, his or her own belonging and belonging to other people to a particular gender; on family composition, kinship and relationships, distribution of family responsibilities, family traditions; about society, its cultural values; about the state and belonging to it; about the world;
mastered the universal prerequisites learning activities - the ability to work according to the rule and on the model, listen to the adult and follow his instructions;
mastered the necessary skills. The child has the skills and abilities necessary for the implementation of various types of children's activities.
In addition, the scientific team of the Research Center "Preschool Childhood" them. singled out the basic characteristics of the child’s personality, which are formed at preschool age, are in constant development, at each age stage they have their content. These personality characteristics, in their essence, constitute the “desired image” of a child of senior preschool age who is ready for school. The basic characteristics of the personality include: competence, emotionality, initiative, independence. In our view, these characteristics define the “model” of a graduate of a modern pre-school educational institution who is able to adapt to the modern information world. The formation of these personal qualities are the result of the implementation of variable educational programs in pre-school education, in a particular institution.
At preschool age, by the age of seven, basic personality characteristics become more meaningful than during the entire preschool childhood: the level of arbitrariness and freedom of behavior increases significantly, which is associated with the child’s increased capabilities and his self-confidence; there is a more adequate assessment of success in different types of activities (drawing, playing, designing, etc.) and a strong motivation for achievement and success.
Competence
Social competence of the child allows him to understand the different nature of the attitude towards him of surrounding adults and peers, his attitude towards them and choose the appropriate line of conduct. The ability to notice changes in the mood of an adult and a peer becomes important, to take into account the wishes of other people; ability to establish stable contacts with peers.
Communicative competence is manifested in the possible free dialogue with peers and adults, the expression of their feelings and intentions with the help of speech and non-speech (gestural, mimic, pantomimic) means.
By the age of seven, the child clearly shows self-confidence and self-esteem, the ability to defend his position in joint activities. Dignity is the most valuable quality of the individual, which requires the support of all employees of the educational institution and parents.
Intellectual competence of senior preschoolers is characterized by the ability for practical and mental experimentation, generalization, the establishment of cause-effect relationships and speech planning. The child shows awareness in different spheres of life: knows about some natural phenomena and their patterns, is familiar with the universal sign systems - the alphabet; numbers, etc. The older preschooler is fluent in speech (has a fairly large vocabulary, grammatically builds sentences, has a well-developed phonemic ear) and has an idea of sound, word, sentence.
The competence of the physical development of an older preschooler is defined as the increased ability to own one's body, various kinds of more and more perfect movements. He has knowledge about his body, about a healthy lifestyle and the need to care about his health. Senior preschooler owns cultural and hygienic skills and understands their need.
Emotionality
A child of preschool age is distinguished by a great wealth of experiences, a variety of their manifestations and at the same time a large manifestation of the arbitrariness of the emotional sphere. Psychologists emphasize the emergence of one of the most important mental neoplasms - "emotional anticipation" - premonitions of their own experiences and experiences of other people related to the results of activities.
Empathy at this age is manifested not only in sympathy and empathy for another person, but also in helping him.
Creativity
A child is capable of creating a new pattern, design, image of fantasy, movement, etc., which are distinguished by originality, variability, flexibility and mobility. The child on the threshold of the school is more and more active, ready for spontaneous decisions, curious, asks questions to an adult, is capable of verbal commenting on the process and the result of his own activities, has a strong achievement motivation, developed imagination. The process of creating a product is creative and exploratory in nature: the child is looking for different ways to solve the same problem.
Arbitrariness
A seven-year-old preschooler is capable of volitional regulation of behavior, overcoming immediate desires, if they contradict the established norms, the rule. Shows strong-willed efforts in situations of choice between “can” and “not”, “want” and “should.” Shows perseverance, patience, ability to overcome difficulties. It can restrain itself, make requests, suggestions, disagreement in a socially acceptable form. The arbitrariness of behavior is one of the most important indicators of psychological readiness for school.
Initiative
Initiative is manifested in all kinds of child's activities: in communication, subject activity, play, experimentation, etc. He can choose the type of activity at will, engage in conversation. Initiative is connected with curiosity, inquisitiveness of mind, ingenuity.
Children's initiative, freedom, reasonable and morally directed, needs a benevolent direction from adults who must support and develop these personality traits.
Autonomy and responsibility
The child’s independence is manifested in the ability without the help of an adult to solve various tasks that arise in everyday life (self-care, caring for plants and animals, creating an environment for amateur playing, using simple safe devices - turning on the lights, TV, player, etc.). An independent child is not afraid to take responsibility, can correct the mistake.
The responsible child seeks to do well the work assigned to him, meaningful not only for him, but also for others; feels with a sense of satisfaction.
Self-esteem
A child of seven years adequately assesses the results of his activity in comparison with other children, which leads to the formation of ideas about himself and his abilities. But psychologists emphasize important psychological feature: characterized by high overall self-esteem, which affects his positive attitude towards himself ("I do not draw very well, but I am good").
Freedom of conduct
This complex concept is based on the competence and upbringing that is formed in the child. A free child is distinguished by internal looseness, openness in communication, sincerity in expressing feelings, truthfulness. At the same time, the child is cautious and prudent, avoids injuries, shows reasonable caution in unfamiliar surroundings, when meeting with strangers. A preschooler can fulfill the rules of behavior developed by society. The upbringing of a sense of security and freedom of behavior in a preschooler relies on an understanding of cause-effect relationships in a wide variety of life situations.
The requirements for graduates can be supplemented in accordance with the specifics of the goals of education in each preschool educational institution. In this case, it is necessary to differentiate the qualities of the graduate, depending on the type and purpose of the educational institution.
Section 5. Aims and objectives of the educational process.
The purpose and tasks of the educational process in each specific pre-school educational institution must be determined in accordance with the developed “model” of the graduate and the determination of the place of each pre-school educational institution in the educational space of the city and the immediate social environment.
The educational program of kindergarten № 5 "Oak" stanitsa Arkhangelsk
|
Section 1. Explanatory note …………………………………………. | ||
|
1.1. Actuality …………………………………………………………… .. | ||
|
1.2. Description of the “graduate model” …………………………………. | ||
|
1.3. Goals and objectives of the educational program ................................... | ||
|
Section 2. Educational programs and their methodological support …………………………………………………………………. | ||
|
2.1.Selection of programs and pedagogical technologies, their integration and methodological support ……………………. | ||
|
2.2. Alignment of the holistic pedagogical process ............ | ||
|
Section 3. Organization of the educational and preschool educational process …………………………………………………… | ||
|
3.1.Design and planning of the current pedagogical activity ………………………………………………………………… | ||
|
Section 4. The monitoring system of children’s achievement of the planned results of program development …………………………………………… | ||
|
Section 5. Conditions for the implementation of the educational program ………. |
The structure of the educational program dou
Key provisions Section 1. Explanatory note 1.1. Urgency: - Age and individual characteristics of the contingent of children - Social order, educational needs of parents - Purpose of pre-school, main means of implementation - Priority areas of activity - Features of the educational process (national, cultural, demographic, climatic) - Principles and approaches to the formation of the program 1.2 Description of the “graduate model” 1.3. Goals and objectives of the educational program Section 2. Educational programs and their methodological support2.1.Selection of programs and pedagogical technologies, their integration and methodological support. 2.2. Building up a holistic pedagogical process.
Section 3. Organization of the educational and preschool process.3.1. Design and planning of current educational activities. 3.2.Content of psychological and pedagogical work on the development of children's educational areas
Section 4. The monitoring system of children's achievements of the planned results of program implementation
Section 5. Conditions for the implementation of the educational program.
BASIC PROVISIONS OF THE EDUCATIONAL PROGRAM
1.1. The educational program of MDOU № 5 "Oak" Art. Arkhangelsk developed in accordance with paragraph 5 of Article 14, paragraph 1 of Article 9 of the Law of the Russian Federation "On Education", the Model Regulations on DOE and federal government requirements for the structure of the basic general educational program of preschool education.
1.2. The educational program of kindergarten № 5 "Oak" Art. Arkhangelsk developed on the basis of exemplary basic general educational programs of preschool education.
1.3. The educational program of kindergarten № 5 "Oak" Art. Arkhangelsk - a document that defines the specifics of the organization of the educational process in pre-school, content of education, forms of organization of activities of preschool children and is aimed at the formation of a common culture, the development of physical, intellectual and personal qualities, the formation of prerequisites of educational activities that ensure social success, preservation and strengthening health of children of preschool age, correction of deficiencies in the physical and mental development of children.
1.4. The educational program of kindergarten № 5 "Oak" Art. Arkhangelsk provides for the construction of a holistic pedagogical process, includes a set of educational areas that ensure the diverse development of children, taking into account their age and individual characteristics in the main areas: physical, social and moral, artistic and aesthetic, cognitive and speech.
1.5. The educational program of kindergarten № 5 "Oak" Art. Arkhangelsk covers all the main points of life of children of preschool age.

 Live journal
Live journal Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter