Sections of the work program for FGOS. Developing a work program for phgos correctly


As regulatory documents the underlying work programs can be:
- FSES LLC;
- OOP LLC educational institution, including the curriculum of basic general education, the program for the development of universal educational activities;
- Federal list of textbooks;
as well as the following materials:
Approximate curriculum subject;


The structure of the work program
The work program of the subject is being developed at
the basis of the current federal state educational standard (GEF), sample and author's program on the subject for each class or parallel, taking into account:
The goals and objectives of the basic educational program of the corresponding degree of general education of the OU;
GEF requirements to the level of achievement of graduates of the corresponding level;
The maximum amount of educational material for students;
The volume of hours of study load on the school subject, determined by the OS curriculum for the corresponding level;
Individual features and cognitive interests
students;
Approved in the OS list of textbooks

- title page;
- explanatory note;
- thematic lesson plan;
- planned educational outcomes;
- educational and methodological support of the educational process;
- material and technical support of the educational process;
- list of changes to the work program.

- the name of the educational institution in accordance with the Charter;
- vultures of approval and approval in accordance with the approval procedure adopted at the educational institution of the University;
- name of the school subject with indication of the class (parallel) for which the Work Program is designed;
- FULL NAME. the teacher who developed the work program;
- the year of the work program.

- regulatory documents and materials on the basis of which the Work Program was drawn up, incl. information about the author's program with an indication of its bibliographic data;
- about the number of class hours per year, the week for which the subject is taught;
- about the goals and objectives of educational activities on the subject in this class, which the work program is aimed at; about the changes made by the teacher in the author's program on the subject, if any, and the rationale for their expediency;

- about the used forms, methods and means of evaluating the educational results of students (including metasubject) at various stages of the implementation of the Work Program: monitoring, intermediate and final certification of students (in accordance with the Regulations in the educational institution, the system for assessing the achievement of the planned results general educational program of general
education), as well as the number of hours to conduct control activities;
- about the forms, methods and means of education, technologies that the teacher plans to use when organizing the educational
process in this class in order to implement the systemic
activity approach, as well as the number of hours for laboratory, practical work, excursions, research projects, etc.

- It is prepared for the academic year and is drawn up in the form of a table, it is an obligatory part of the work program.
- Since the development of work programs is the competence of the educational institution, the format of the presentation of the thematic plan is determined in the school and should be recorded in the "Regulations on the work program." However, when determining the format of a thematic lesson plan, it should be borne in mind that must necessarily reflect the following information : the name of the section (topic) and the duration of its study, the lesson number, the topic of the lesson ”, the topics of lessons - examinations, lessons - practical (laboratory) works and other types of activities of students, planned results of the study section.
- In the future, the recording of the title of the lesson topic in the educational journal should fully coincide with the wording of the lesson themes in thematic lesson plan.

The planned educational results of students
- This must structural component of the work program
reflects the list of requirements for personal, metasubject,
subject results to which it is aimed.
- The planned results of the implementation of the work program in this class are drawn up taking into account the requirements of the Federal State Educational Standard, the program for the development of universal educational activities, the author's program.
- Meta-subject and personal educational results should be specified in the form of a list of relevant universal educational actions (metasubject - in the form of communicative universal educational actions, cognitive universal educational actions, regulatory universal educational actions; personal - in the form of personal universal educational actions)

Educational and methodological support of the educational process
The component should reflect the main and additional educational literature, other information sources for
students who the teacher plans to use to implement the work program.

Material and technical support of the educational process
The component should reflect the list of educational equipment and equipment for laboratory, practical
works, organization of project and research activities

Change Sheet
Must be in the format of lesson thematic plan. It is provided
to record possible changes in the Work Program, the need for which may arise during the school year.
The teacher has the right to make changes to the Work Program only on the basis of an order from the head of the educational institution or subject to agreement with the head teacher for educational work.

Work Program Approval Procedure
- The first stage (the time is indicated) - The work program is examined in a methodical association of teachers (the level is indicated - municipal, school).
- The second stage - (the deadline is indicated) - the work program is reviewed at the pedagogical council, the results are recorded in a protocol;
- The third stage - (specifying a period) - The work program is approved by the head of the educational institution.
- After approval by the head of the educational
institutions The work program becomes a regulatory document implemented in this educational institution. After the approval of the Work Program, the teacher is not entitled to make changes to it without the consent of the administration of the educational institution.

Making work program
- The work program is issued on paper and electronic media. The paper version is made on white A4 paper. Border width: left - 30 mm, right - 15 mm,
top - 20 mm, bottom - 20 mm
- The font of the main text and notes - Times New Roman. The font size of the main text - 14 pt, in the tables - 12 pt, in the headings of the tables - 12 pt. Inscription - the usual.
- Line spacing in the main text and in the tables - single. Alignment of the main text - in width, headings - in the center. Paragraph indents in the main text - 1.25 cm.
Section headings (parts) are printed in boldface type in capital letters without underscores, and
headings of subsections (paragraphs, etc.) - with a capital letter without underscore.
- Sheets are numbered in Arabic numerals in the upper part of the sheet in the center.
Structure of the GEF work program
The regulation on the structure of the work program is formed in accordance with the sectoral legislation, the charter of the educational institution and other regulatory, local documents. This article sets out what constitutes the structure and content of the work program.
General information
First of all, the concept of a work program should be disclosed. It acts as a legal instrument, mandatory to comply in full. The structure of the work program on the subject ensures the implementation of the requirements of the state standard of the second generation. It is formed in accordance with the conditions and results of education on the 1st and 2nd stages. Drawing up a work program is necessary to create conditions for the organization, planning and management of the educational process for a particular discipline (region). It should ensure the achievement of the results of mastering the basic material.
Tasks
The structure of the GEF work program is structured in such a way that:
To form an idea of the practical implementation of standard components in the study of a particular discipline.
Clearly define the essence, order, scope of the course in accordance with the goals, characteristics and objectives of the educational process of the institution and the number of students.
Functions
The structure of the GEF work program implements:
Regulatory function. It is explained in the very definition of this document.
The function of goal setting. This means that the work program establishes goals and values, for the achievement of which it, in fact, is introduced into one or another course.
The function of determining the essence of the educational process. The structure of the work program fixes the composition of the elements that need to be learned, determines the level of their complexity.
Process function Speech in this case is about determining the logical sequence of assimilation of elements, means and conditions, organizational methods and forms of the educational process.
Evaluation function. The document identifies the degree of assimilation of elements, defines the criteria for evaluation and objects for monitoring the level of children's learning.
Compilation
The structure of the working curriculum is formed and approved by the educational institution. The preparation of the document can be carried out both by one teacher and their group. The program should be the same for all specialists in a particular discipline. She serves for the teacher as the basis for the formation of the calendar-thematic plan for the year. If there is no indication in the project of the distribution of hours according to topics and sections, if only their total number is given, the teacher sets them independently. In this case, one should be guided by the appropriate methodological materials and focus on the personal characteristics of children.
Registration
Work programs in mathematics, literature, or another other discipline are performed on the model on a computer. The text should not be corrected. The set is carried out in the Word editor. Font letters should use Times New Roman 12–14. The spacing between lines is single. The text is justified in width, there should be 1-2 cm margins on all sides. Paragraphs and headings are centered using the editor tools. Table insertion is performed directly in the text. The first is considered the title page. It is not numbered. Calendar-themed plan is in the form of a table. The structure of the work program should include a list of references. It is arranged alphabetically with all the output data. The paperwork should be accurate, all information is given in a logical connection with each other. The format of the program is A4. Additional designation for the work program on academic subjects in an educational institution is not provided in the standards.
Scheme
The structure of the work program of the teacher is as follows:
Name of Shelter according to the charter.
The name of the discipline for which the document is created.
An indication of the class for which the program is being compiled.
Grif consideration, approval, approval.
Compilation year.
All this information is indicated on the title page. The structure of the work program of the educator will be different from the presented scheme. They are due to the specifics of the work of the DOW itself.
Sections
All work programs (in mathematics, foreign language, biology, and other disciplines) are accompanied by appendices and explanations. These include:
List of legal acts.
Common tasks of primary and basic education. They must be specified in accordance with the specifics of the course (subject).
General characteristics of the discipline.
Description of the position of the course in the plan.
The exact name of the program in the discipline with bibliographic characteristics.
Statement of values.
Meta-subject, personal, substantive results of mastering a particular discipline.
Description of the regional component. It is issued by the table.
Calendar-themed plan. At the same time, the main types of educational activities with a description of the expected results of development should be identified.
Requirements for the level of training of children.
Description of control and measuring materials.
Explanations
The structure of the work program of the teacher must meet the requirements of standards. The material of the educational course is aimed at providing conditions for the formation of individual and metasubject (universal) actions. In this regard, in the appropriate section should list the EAL, which are performed during the development of a particular course. In addition, there are types of tasks and techniques in which the formation of universal actions is designed.
Learning sequence
The structure of the work program includes the rationale for selecting hours by section and year. It should disclose the sequence of mastering the material, show the distribution of time, taking into account the maximum load. In the description of the content of sections (themes) the following sequence is established:
Name.
The required number of hours.
Expected mastering results are presented taking into account the specifics of the subject (“a graduate will learn / will be able to learn ...”).
Methodical support
This section describes the characteristics of the corresponding complex. The list of educational and methodological support should include such materials as:
Theoretical (textbook, program).
Didactic and methodical (manuals for teachers, collections of test / test works, notebooks for independent work).
Other sections
When describing the part of practical exercises, you should indicate the number of them, which is necessary according to the program, and which are distributed by topic. In the section of mastering the level of assimilation, a complex of measuring materials is included (tests, practical / test works). For each discipline provides its own forms:
In the Russian language - dictations, tests, essays, tests, check cheating, narration.
On physical education - standards of physical training.
In mathematics - independent / test papers, testing, and so on.
The structure of the work program should include measuring materials that meet the standard. Forms created by the author of the project should be given in the appendix.
Explanatory note
It should indicate:
Addressee (type and type of educational institution, class.
Features of the program regarding GEF.
The main idea of the project.
The validity of the program.
The area in which a particular course is included.
Brief formulation of common goals for education.
The term of the project.
Key criteria for the selection of materials, explanation of the logic of building a program. In this section, among other things, the links of the main and additional courses on the discipline (if any) are disclosed.
Scheduled results.
A summary of the assessment system.
Description of the main analysis tools.
Presentation of the system of symbols.
Characteristics of the course
This section contains information about:
The main technologies, forms, methods, mode of employment.
The logical connections of the subject with other disciplines / sections of the plan.
Development results
This section describes the requirements:
To the preparedness of children enrolled in the program. The results of mastering are specified for a particular class and can be differentiated by levels.
To the preparation of students in the discipline, which fully coincide with the requirements of the standards and the author's (approximate) program in the subject or educational projects.
Which are set in the form of activity (which, as a result, graduates should be able to know, use in practice, in everyday life).
Description of topics
The work program contains lists and names of sections, topics of discipline, the required number of hours. The content of the topic indicates:
Key questions to explore.
Laboratory and practical work, creative tasks, excursions and other forms used in training.
Requirements for skills and knowledge of students to complete the study.
Questions and forms for control.
Estimated types of independent work of students.
Formed Uud.
Calendar-themed plan
It is compiled indicating the key activities of children:
List of sections, order, sequence of study material.
The number of hours for each item.
Topics for individual lessons and materials to them.
Type of occupation (practical, theoretical), number of hours.
Types of schoolchildren activities.
Control methods and forms.
Applications
They can be presented in the form:
Project themes.
The basic concepts used in the course.
Control and measuring materials.
Those creative tasks.
Examples of work.
Texts dictations, checks, testing, etc.
Responsibility of the educational institution
It is set in the Federal Law "On Education". According to its provisions, the educational institution will be responsible for the implementation of curricula that do not fully comply with the curriculum and the schedule of the educational process. In the course of drawing up his project, the teacher must take into account the requirements of state standards. The main principles of the implementation of the GEF discipline are:
Reflection of the planned results in the main educational direction (for a particular discipline).
Creation of conditions ensuring the achievement of established regulatory indicators for the development of the course.
Inclusion in the content of the program being developed all the didactic elements of an exemplary project on a specific subject.
Review and approval
The work program on the subject is discussed at a meeting of methodical school associations. The project is coordinated with the head of MO. In particular, the date, number of the protocol that was kept at the meeting shall be entered, the signatures of authorized persons shall be put The work program is agreed by the deputy director for educational work. After this, the project is approved by the director of the educational institution itself. On the title page affixed stamp.
Conclusion
The structure of the program thus reflects all aspects of the educational process specifically on the subject. The preparation of this document provides the clarity and consistency of the actions of the teacher, allows you to provide for different situations. In the formation of the program takes into account the individual characteristics of children, the specificity of the discipline. Developing a program is of crucial practical importance. It not only describes the features of the discipline, the methods of studying and presenting the material, but also establishes the results that graduates should achieve. The introduction of programs into the practice of the work of teachers has a stimulating effect on them. Through an analysis of the final results, teachers see the effectiveness or inefficiency of certain tools and tools, find errors, problems, ways to eliminate them. It is also important that the implementation of the work program is carried out with the active participation of schoolchildren. The document provides for a variety of forms and types of actions of children, contributing to the assimilation of the material.
Download:
Preview:
The structure of the work program for the subject,
the course in accordance with the requirements of the GEF LLC
The work program is a document created on the basis of an exemplary or author's program, taking into account the goals and objectives of the educational program of the institution and reflecting the ways of implementing the content of the school subject.
The work program is drawn up for the academic year or grade level. The work program is developed by each teacher independently for each class (parallels). The basis for the development of curriculum programs are the requirements of the GEF.
Programs of individual subjects are developed on the basis of the requirements for the results of mastering the main educational program, taking into account the main directions of the programs included in the structure of the main educational program.
Programs of individual subjects, courses should contain:
1) title page
2) an explanatory note, which specifies the overall objectives of basic general education, taking into account the specifics of the school subject;
3) the general characteristics of the school subject, course;
4) a description of the place of the school subject, the course in the curriculum;
5) personal, metasubject and subject results of mastering a particular academic subject, course;
7) thematic planning with the definition of the main types of educational activities;
8) a description of the educational and methodological and material and technical support of the educational process;
9) the planned results of the study of the academic subject, course.
The structure of the work program (GEF LLC)
1. On the title page indicated:
name of the educational institution (in full);
fields for program approval / approval;
name of the program (subject, course); targeting (class or grade level)
the name of the settlement in which the work program is implemented;
year of work program development
2. Explanatory note
The text of the explanatory note should indicate:
Compliance of the work program with the federal component of the state educational standard of general education
Regulatory acts and educational and methodological documents on the basis of which a work program has been developed (GEF, the corresponding Model OOP, an exemplary curriculum for the subject, the author's program);
General goals of education, taking into account the specifics of the school subject, course;
The role of the training course, the subject in achieving the planned results of mastering the main educational program of the school (the program’s focus on the formation of personal, metasubject and subject results of the development of a particular subject, course is indicated);
3. General characteristics of the school subject
In this section, it is necessary to disclose the role and importance of the subject in terms of the goals of general education (based on the concept of the corresponding GEF), modern requirements for graduates. It shows the continuity in the study of this subject, the course in primary and basic school, accents are placed in the implementation of the connection of training in the subject with practice and with current problems of our time.
4. Description of the place of the school subject, course in the curriculum.
The section indicates the number of hours allocated to this subject in accordance with the curriculum.
5. Personal, metasubject and subject results of mastering a particular academic subject, course.
It is necessary to include in the work programs not generalized requirements for the results formulated in the GEF, but to include the wording of the results from the author's programs (V.Voronkova) or approximate OOP of the corresponding level of general education. This section reflects
- personal, metasubject and subject results of the development of the school subject, course, consistent with the previously set goals of mastering the work program.
The description of the content indicates the sections and topics of study of the subject necessary to implement the requirements of the standard.
If the sample or the author's program does not specify the distribution of hours for sections and topics, but only the total number of hours is indicated, the teacher in the work program distributes the hours into sections and topics independently, focusing on the educational and methodical complexes used. The content of the school subject includes:
The name of sections of the curriculum and the characteristics of the main content lines,
The list of laboratory and practical work, excursions,
Directions of project activities of students,
Use reserve training time.
7. Thematic planning with the definition of the main types of educational activities (for the academic year)
The form of thematic planning can be repeated by the author with the necessary adjustments made by the teacher.
The structure of the calendar - thematic plan is determined by the educational institution independently.
Thematic planning with the definition of the main activities of students (at the level of educational activities): sections of the program; topics included in this section; main content by topic; the characteristic of the main activities of the student (at the level of educational activities), universal educational activities mastered in the framework of the study of the topic.
Thematic planning, as well as the entire work program, is drawn up for one academic year.
8. Description of the material and technical support of the educational process (to the level of education)
The section indicates:
Teaching tools: teaching and laboratory equipment and devices, technical and electronic means of teaching and controlling students' knowledge, educational and reference books, digital educational resources, demonstration and handout didactic material;
The list of recommended educational and methodical literature should contain the teacher-methodical complex used by the teacher with the obligatory indication of a textbook, teaching aids for students, and also contain complete literature output data;
Additional literature for teachers and students;
The list of training reference information, monitoring and other computer programs used in the educational process; (tabular version is possible.)
In the list of references, the description of each work must be listed in alphabetical order and meet the requirements for bibliographic description. Example: Gorsky D .., Ivin A.A. A brief dictionary of physical education. - M: Enlightenment. 2006. Registration of the list of references on the main sections of the studied subject is allowed.
9. The planned results of the study of the school subject
(per training level)
In the basic educational program of the basic general education of the school in the item “Planned results of the development of the PLO” the results at the end of the course are given, that is, for the basic school this is the end of the 9th grade. All formulations in this paragraph, as well as in the work program, are written by year.
For the baseline results, “graduate will learn,”
For a higher level of results, "the graduate will have the opportunity to learn."
The system of evaluation of the planned results, expressed in the forms and types of control, in the definition of test and measuring materials, in terms of the level of success of students (“good / excellent”, rating, portfolio, etc.); features of an assessment of the individual project and individual achievements of students.
Applications to the program
(per class)
Basic course concepts; - themes of projects; - themes of creative works; - methodical recommendations, etc.



![]()
















1 of 21
Presentation description for individual slides:
Slide number 1
Description of the slide:
Working programm. Structure. Biology teacher MBOU SOSH number 37 Kartashova Maria Alekseevna
Slide number 2
Description of the slide:
MBOU School № 37 Kartashova M.A. The structure of the Program is a form of presentation of a school subject (course) as an integral system, reflecting the internal logic of organizing educational material, and includes the following elements: 1. Title page (program name). 2. Explanatory note. 3. Training and thematic plan. 4. Content of the training course. 5. Requirements to the level of training of students in this program. 6. The list of educational support. 7. References (main and additional). 8. Applications to the program.
Slide number 3
Description of the slide:
MBOU School № 37 Kartashova M.A. The title page is a structural element of the program, representing information about the name of the program, which should reflect its content, place in the educational process, and targeting. The title page indicates: the name of the Program (subject, course); targeting (class or stage of study, or age of students); information about the author (name, title, qualification category or grade); year of the program. Title page
Slide no 4
Description of the slide:
MBOU School № 37 Kartashova M.A. (Educational Institution) “Agreed” “Approved” Director of GOU Secondary School No. Head of Methodological Association (Current Year), (Current Year), (Work Program) ((Textbook) (Textbook Status)) Developer Program Teacher (Last Name) (Name ) (Patronymic) Pedagogical experience (Pedagogical experience) years, (Qualification category). (Current year) year
Slide number 5
Description of the slide:
MBOU School № 37 Kartashova M.A. Explanatory note - a structural element of the program, explaining the relevance of the study of this course, its objectives and specificity, as well as methods and forms for solving the tasks (practical tasks, independent work, training, etc.), recommendations for their implementation. For compiler programs, the output data of the materials (programs, manuals, etc.) that were used in the preparation of the program should be indicated. In the Explanatory Note, the proposed content and scope of the course should be justified, the number of hours devoted to the study of this course according to the curriculum, forms of control and possible options for its implementation should be indicated. The number and nature of control measures to assess the quality of student preparation should be clearly justified. At the same time, it is necessary to indicate how these measures allow to reveal the compliance of the results of education with the goals and objectives of the training. Explanatory note
Slide no 6
Description of the slide:
MBOU School № 37 Kartashova M.A. The text of the explanatory note indicates: the title, author and year of publication of the model (model), author's curriculum, on the basis of which (s) the work program is developed; the goals and objectives of this training program in the field of the formation of a system of knowledge and skills (the tasks are formulated in accordance with the state educational standard and taking into account the specifics of this OC); changes made to the sample (model) or the author's curriculum, their rationale; training kit (textbook, workbook, test book, atlas, contour map, etc. according to the list of textbooks approved by order of the Ministry of Education and Science of Russia) used to achieve the goal in accordance with the educational program of the educational institution (indicated: F.I. O. author of the manual, title, class, publisher, year of publication); the number of study hours for which the work program is designed, including the number of hours for control, laboratory, practical work, excursions, projects, research; features, preferred forms of organization of the educational process and their combination, as well as the prevailing forms of current control of knowledge and skills (in accordance with the Regulations on the current control of students, intermediate certification of students in the OU
Slide no 7
Description of the slide:
MBOU School № 37 Kartashova M.A. The curriculum is a structural element of the program, containing the name of the topic, the total number of hours (including theoretical and practical classes). Drawn up as a table. The curriculum and thematic plan reflects the sequence of study of sections and themes of the program, shows the distribution of training hours, determines the conduct of tests, control, practical and other types of work. A training and thematic plan is drawn up for the entire period of study (usually for an academic year). Training and thematic plan Section Topic Number of hours Including, counter. slave
Slide number 8
Description of the slide:
MBOU School № 37 Kartashova M.A. The course content is a structural element of the program, which includes the interpretation of each topic, according to the numbering in the curriculum. The content of the curriculum of the course, subject, discipline (module) includes an abstract description of each section according to the numbering in the curriculum. The presentation of educational material in a given sequence provides for the specification of all didactic content units. Course content
Slide number 9
Description of the slide:
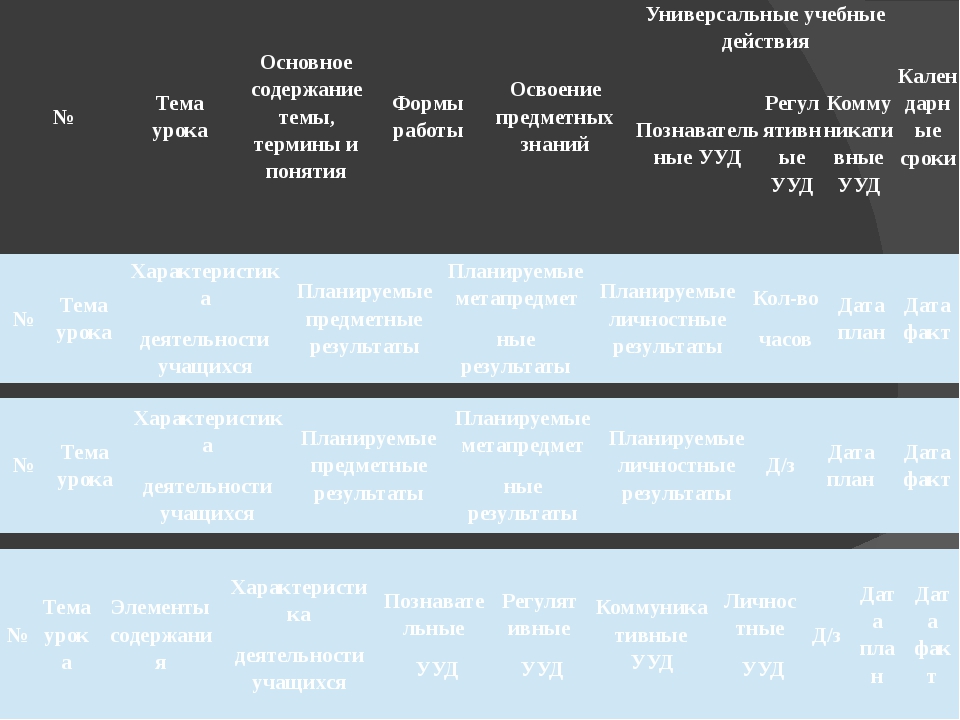
MBOU School № 37 Kartashova M.A. № Theme of the lesson The main content of the topic, terms and concepts Forms of work Mastering subject knowledge Universal learning activities Calendar dates Educational CRA Regulatory CRA Communicative URD No Lesson topic Characteristic activity of students Planned subject results Planned metrological results Planned personal results Number of hours Date plan Date fact № Topic of the lesson Characteristic of the activities of students Planned subject results Planned metasubject results Planned persons BEST RESULTS D / C Date Plan Date Act No Lesson Topic Content Elements Characteristics of Students' Activities Cognitive UL Regulatory UCD Communicative UUD Personal UL D / C Date Plan Date Actual
Slide no 10
Description of the slide:
MBOU School № 37 Kartashova M.A. № Date Lesson topic Solved problems (goal) Concepts under study Object result UUD Personality result № Date Lesson topic Solved problems (goal) Concepts under study Subject result UUP Personality result Out-of-school activity № Lesson theme Elements of educational content Type of activity of students Subject result Meta-subject URD Form of diagnosis and control Date plan Date fact № Lesson theme Elements of educational content Characteristics of students' activities Subject results Meta-subject results s Personal Date of Plan Date of fact
Slide no 11
Description of the slide:
MBOU School № 37 Kartashova M.A. The structural element of the work program "Controls" includes a system of control materials (tests, tests, test questions, etc.) for assessing students 'mastery of the planned content, presented in the form of a list of students' actions as goals and learning outcomes. Oral control materials represent A list of questions and tasks. Written control materials may contain a codifier (range of skills tested), options for work, a scheme for analyzing work. materials is determined by the training and thematic plan. So, if the plan provides for carrying out 5 tests, then 5 work packages are attached to the work program.
Slide number 12
Description of the slide:
MBOU School № 37 Kartashova M.A. Requirements for the level of training of graduates enrolled in this program is a structural element of the program that determines the basic knowledge and skills in skills that students must master in the process of studying this course. The structure of the work program "Requirements for the level of student preparation" is a description of the goals and learning outcomes expressed in the actions of students (operational) and actually identifiable using any tool (diagnostic). This list of goals and learning outcomes includes special subject and general educational skills and methods of activity. The basis for the selection of requirements for the level of training of students is the state educational standard of general education and the curriculum (approximate (typical) and (or) author's), on the basis of which (s) a work program is developed. Therefore, the requirements for the level of training of students, written in the work program, should not be lower than the requirements formulated in the federal component of the state standard of general education and the curriculum adopted as the basis. When developing requirements for the level of training of students, it is necessary to take into account the peculiarities of their formulation. Namely, the requirements must: be described through the actions of the students; indicate a certain level of achievement; be achievable and evaluable; be clear to learners.
Slide number 13
Description of the slide:
MBOU School № 37 Kartashova M.A. General learning objectives, verbs for the formulation of specific learning outcomes and key questions for assignments to identify their presence or absence (according to B. Bloom's taxonomy) Levels of learning goals (content assimilation level) General learning goals Verbs for formulating specific learning goals-outcomes Key questions for tasks 1. Knowledge of the Category designates the memorization and reproduction of the material studied - from specific facts to a holistic theory. Knowledge of specific data Knowledge of means and methods of action with specific data Knowledge of categories and general concepts Defines, selects, indicates, selects, (meaning the term), names (specific fact, date, event, place); states (fact) Identifies (character), lists (process steps), describes (method) Quotes (rule), sets out (principle, law, theory), recalls the name (theory), reproduces (structure) How much ... Who ... What ... When ... Who ... Where ...
Slide no 14
Description of the slide:
MBOU School № 37 Kartashova M.A. 2. Understanding An understanding of the material can be the transformation of a material from one form of expression into another, the interpretation of the material, the assumption of the further course of events and events. Translation Interpretation Extrapolation Restructure (in abbreviated form), reformulate, retell (in their own words), give examples, translate (table into graph) Distinguishes (essential, insignificant) explains (diagrams and graphs, use of methods), summarizes, summarizes (facts) Shows , fixes the consequences (of these facts). What example corresponds to ... What is the main idea ... Do I understand correctly what it means ... Can you explain ... How can you paraphrase (summarize) ... 3. Application This category means the ability to use the studied material in specific conditions and new situations. Application of knowledge in practice Changes, counts, demonstrates (correct use of a method or procedure), detects, manipulates, modifies, acts, prepares, produces, relates, shows, solves, uses (concepts and principles for analyzing new situations), applies (laws and theory of practice situations). What will be the result, if ... How to apply for ... Can I use ... for ... How can I solve ... a problem using knowledge of ...
Slide number 15
Description of the slide:
MBOU School № 37 Kartashova M.A. 4. Analysis This category means the ability to break up the material into components so that the structure clearly appears. Analysis of elements Analysis of relations Analysis of organizational principles Distinguishes (logical errors, positions, assumptions, etc.); differentiates, highlights (model components); recognizes (hidden values); identifies (assumptions, reasons), highlights (similarities and differences); recognizes (prejudice, bias), distinguishes (facts from opinions) Reveals, schematizes connections (between facts and consequences); reconstructs (interactions and relationships); compares (hypothesis with this information) Schematizes (model), identifies (structure of work) How to ... relate to ... What is the difference ... What are the main assumptions ... What are the possible motives ... What are the components ... How can I classify ... What evidence can I give ... What testifies about ... What is the relationship between ... 5. Synthesis This category means the ability to combine elements in order to obtain a whole that is new. Getting new knowledge based on mastered skills Generates (unique message, original idea), creates (apparatus, method, model), develops (a scheme for classifying information, model), composes (poem, story, essay), plans, compiles (experiment plan ), integrates (problem solving), combines, develops (a scheme for classification), combines, summarizes (knowledge from different areas into a plan to solve a problem), reorganizes, modifies into a new integrity (ideas, material, process), makes deductive conclusions from but bstractions, makes inductive conclusions from specific information. How can you adapt ... to create something else ... What can be proposed to minimize (maximize) ... How can you combine ... What criteria can be combined ... What should be combined to confirm ... How ... to include in ...
Slide number 16
Description of the slide:
MBOU School № 37 Kartashova M.A. 6. Evaluation This category refers to the ability to assess the value of a particular material. Evaluating events, processes, activities Judges, evaluates (logical sequence of written material, compliance of findings with data), compares (ideas), concludes, compares, contrasts, criticizes, describes, distinguishes, recognizes (subjectivism), explains, confirms, interprets, correlates, summarizes , supports, argues, verifies (convincing evidence) You agree ... Why ... Why exactly this is chosen ... Would it be better if ... What can be offered to ... How can it be assessed, from the position ... What are Contradictions ... What are the strengths and weaknesses ... What is the basis of the statement ...
Slide no 17
Description of the slide:
MBOU School № 37 Kartashova M.A. The list of educational and methodological support is a structural element of the program that determines the methodological and teaching aids necessary for the implementation of this course, equipment and instruments, didactic material. Educational and methodical teaching aids include: main and additional educational literature (textbooks, teaching aids, collections of exercises and tasks, control tasks, tests, practical work and laboratory workshops, reading books); reference manuals (dictionaries, reference books); visual material (albums, atlases, maps, tables); programs of information and computer support for the educational process (multimedia textbooks, electronic editions of encyclopedias; educational software development environments); equipment and devices necessary for the implementation of the work program. Used teaching and learning tools can be divided into four groups: Literature (primary and secondary); Didactic materials; Information and computer support for the educational process; Equipment and appliances. The literature is designed in accordance with GOST: elements of the description of each work must be listed in alphabetical order and comply with the requirements for bibliographic description.
Slide number 18
Description of the slide:
MBOU School № 37 Kartashova M.A. References - a structural element of the program, including a list of used by the author of the literature. Elements of the description of each work must be listed in alphabetical order and meet the requirements for bibliographic description. The list of references is constructed in alphabetical order, with an indication of the city and the name of the publisher, year of release, number of pages of the document (book), if it is fully studied. Allowed to make a list of references on the main sections of the studied subject (course). Bibliography
Slide number 19
Description of the slide:
MBOU School № 37 Kartashova M.A. The design of the working program. The text is typed in the Word for Windows editor with the font Times New Roman, 12-14 size, single line spacing, no hyphenation in the text, alignment in width, paragraph 1.25 cm, margins usual upper 2 cm, left 3 cm, right 1.5 cm, lower 2 cm; alignment of headings and paragraphs in the text are performed using Word tools, A4 sheets, landscape orientation. Tables are inserted directly into the text. The work program is stitched, pages are numbered, sealed by the educational institution and signed by the head of the educational institution. The title page is considered the first, but not numbered, as well as application sheets. Making work program
Slide number 20
Description of the slide:
MBOU School № 37 Kartashova M.A. Approval of the work program The work program is approved annually at the beginning of the school year (until September 5 of the current year) by order of the director of an educational institution. Approval of the Program involves the following procedures: discussion and adoption of the Program at a meeting of the subject methodical association; obtaining an expert opinion (approval) from the deputy director in charge of the teacher, subject, course, activity, etc. It is allowed to conduct an examination of the Program with the assistance of external experts. In case of non-compliance of the Program with the requirements established by these Regulations, the head of the educational institution imposes a resolution on the need for improvement with an indication of a specific date of performance. All changes, additions made by the teacher to the Program during the school year must be coordinated with the deputy director in charge of the teacher, subject, course, activity, etc. Approval of the work program
To download the material, enter your email, specify who you are, and click
- Home decor for the new year
- Summary of literacy classes for children of the preparatory to school group "Sound and the letter Y"
- Voicing consonants: examples
- Algorithm for solving the ege on the Russian language
- · · Speech therapy commission in children
- Lexical theme: "Animals of hot countries"
- Recommendations for the development of coherent speech in preschool children

 Live journal
Live journal Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter