The system of teaching methods of training. The concept of "methodical technique"
METHOD - ordered set of use of funds physical culture in the process of forming the physical perfection of man.
METHOD - a system of teacher's actions developed with due account for pedagogical regularities, the purposeful use of which allows organizing theoretical and practical activity of a student, ensuring the development of his motor actions aimed at developing physical qualities and personality formation. (Yu.F.Kurmashin, 2003).
In accordance with the objectives and conditions of training, each method is implemented using methodological techniques. For example, the method of display is carried out by different methods: showing exercises in profile or full face, showing at a certain pace, etc.
METHODOLOGICAL RECEPTION is a way to implement the method in accordance with the specific task of training.
Consequently, various techniques are used within each method. The richer the stock of teaching methods, the wider the range of application of the method.
METHOD - special system methods, teaching methods and forms of organization of classes, aimed at solving the pedagogical problem.
For example, we can talk about the method of teaching a tumbling forward or backward, the method of developing power abilities, the method physical education at preschool institutions and etc.
The term "methodology" means a set of ways appropriate to carry out any work.
The methodology, if possible, should contain an exact prescription on the implementation in a certain sequence of actions (operations) leading to the solution of the stated pedagogical problem.
METHODICAL APPROACH - a set of methods of influence of the teacher on the students, the choice of which is determined by a certain scientific concept, the logic of the organization and the implementation of the process of training, education and development.
For example, when teaching movements, one can use traditional and non-traditional approaches (algorithmic, adaptive-program learning using computer, etc.); When learning motor actions and developing physical abilities, two opposite approaches are possible: analytical (selective) and integral (integral).
More on topic 6.1. The original concepts of "method", "methodical technique", "Methodology":
- S.V. Kazanovich, N.A. Zavapko. Theory and methods of curator work. Teaching guide., 2008
- Ivanenko A.A. Philosophy as a science: the genesis of the scientific method in the works of IG Fichte., 2012
- Averyanov A.P., et al. Methodological guidebook on the new history, 1640-1870: grade 9, 1991
- The team of authors. Pass the exam in pedagogy: Teaching guide., 2005
Methods and techniques of learning
| Parameter name | Value |
| Topic of the article: | Methods and techniques of learning |
| Category (subject category) | Education |
Method learning (from the Greek methodos - “The way to achieve the goal”) is a system of consecutive interrelated actions of the teacher and the students, ensuring the assimilation of educational material.
Method - a multidimensional and multidimensional concept. Each teaching method has many properties and attributes, as a result of which there are many principles of their differentiation. For this reason, in pedagogical science there is no single approach to the selection of teaching methods.
Different authors distinguish the following teaching methods: story, explanation, conversation, lecture, discussion, work with a book, demonstration, illustration, video method, exercise, laboratory method, practical method, test work ͵ survey (variations: oral and written, individual, frontal, compacted), programmed control method, test control, abstract, didactic game, etc.
Posted on ref.rf
This list is far from complete.
In the process of learning, the teacher uses various methods: story, work with a book, exercise, demonstration, laboratory method, etc.
Posted on ref.rf
It is important to remember that no method is universal, that is, a single method will not give the necessary results in full. Good results in training can be achieved only when using a number of methods that complement each other.
The effectiveness of teaching methods in any pedagogical situation depends on the specific goals and learning objectives. The most important component of pedagogical competence is the ability of the teacher to choose and apply teaching methods correctly.
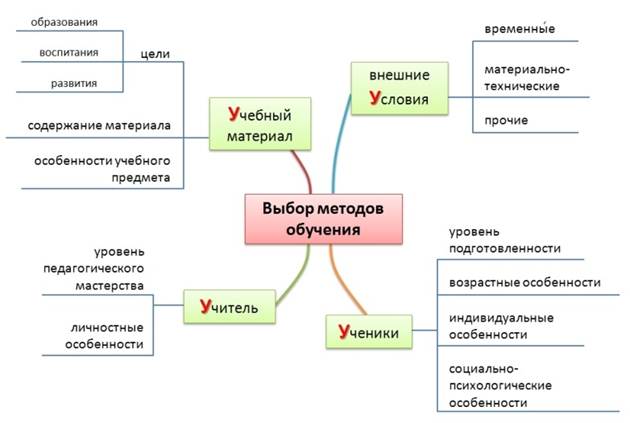
The choice of teaching methods is due to a number of factors, including:
goals of education, upbringing and development of students;
features of the content of the studied material;
features of the teaching methodology of a particular school subject;
the time allotted for the study of a material;
the level of preparedness of students, their age characteristics;
level of pedagogical mastery of the teacher;
material and technical conditions of education.

Fig. 4.4. Selection of teaching methods
Methods of teaching in work practice are realized with the help of methods and means of training, ᴛ.ᴇ. the method in its specific embodiment is a combination of certain techniques and means.
Learning techniques (didactic techniques) are usually defined as elements of methods, single actions as part of a general teaching method. The method is ϶ᴛᴏ not yet a method, but its constituent part, but the practical implementation of the method is achieved precisely with the help of methods. So, in the method of working with a book, the following techniques can be distinguished: 1) reading aloud; 2) drawing up a text plan; 3) filling in the table on the material read; 4) drawing up a logical scheme of reading; 5) note taking; 6) selection of quotes, etc.
Acceptance of training can be considered as a separate step in the practical application of the method. The sequence of these steps in the process of implementing the method leads to the goal of learning.
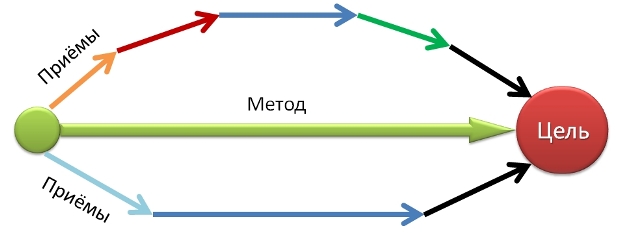
Fig. 4.5. The ratio of reception and method
The same method in various situations can be carried out using different techniques. For example, working with a book in one case may include reading out loud and drawing up a plan of text ͵ in another case, drawing up a logical scheme and selecting quotes, in the third case taking notes.
The same technique can be part of different methods. So, drawing up a logical scheme can be part of an explanatory and illustrative method (for example, a teacher explaining a new material, drawing a scheme on the blackboard), and can also be used as part of a research method (for example, students make a diagram reflecting the material they independently study) .
Teaching methods are developed in the experience of many teachers and improved over decades. Many of the modern methods appeared many centuries ago. For example, the story and exercise were already known in the schools of the Ancient World, and in Ancient Greece, Socrates perfected the method of conversation and began to use it to develop thinking and enhance the cognitive interest of students. Unlike methods, techniques can be created in the experience of an individual teacher, determining the uniqueness of his individual pedagogical style.
There are relatively few methods, but there are countless methods, and therefore it is very difficult to classify methods and it is almost impossible to compile a complete, exhaustive list of all didactic methods. In fig. 4.6. Only some groups of learning techniques are presented.
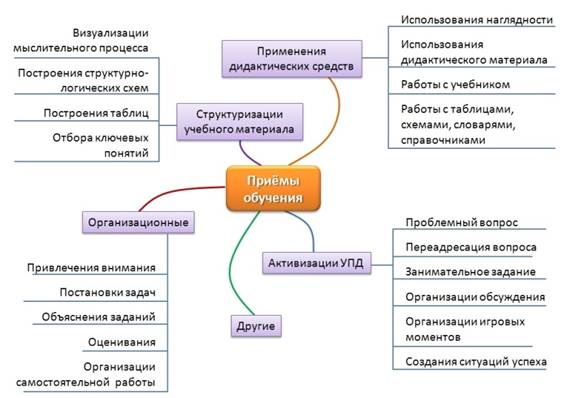
Fig. 4.6. Types of learning techniques
Methods and techniques of learning - the concept and types. Classification and features of the category "Methods and techniques of learning" 2014, 2015.
Teaching methodsTeaching methods are understood as the relationship between a teacher and children, purposeful actions of an adult, which allow a child to learn basic knowledge about music, to acquire practical skills and abilities that help develop musical abilities.
Methods of musical education and training are united in their pedagogical orientation. Therefore, training is both upbringing and developing. Knowledge and skills acquired by children in the learning process help them to actively express themselves in singing, dancing, playing instruments and, thus, successfully solving educational tasks of general and musical-aesthetic development.
Well-known teachers in the field of the theory of general and preschool pedagogy B. P. Esipov, M. A. Danilov, M. N. Skatkin, A. P. Usova, A. M. Leushin, and others emphasized that the methods depend on the educational tasks, from the content of the subject, from the age of pupils.
This also applies to music education, where the methods of learning tasks used depend on specific types musical activities, ways of information, age characteristics of children.
The purpose of educational tasks is to learn the repertoire (songs, games, round dances, etc.) and master the elementary musical knowledge, skills and abilities.
Let us consider an approximate scheme, according to which it is possible to compare educational tasks and teaching methods (see Table 2, p. 34).
In the proposed scheme, only outlined the methods that allow to perform training tasks. Learning assignments are not an end in themselves. This is only a means of educating the children of a moral and aesthetic attitude to music, the development of creative actions, the ability to respond emotionally to music, to express their own assessment. On practice studying proccess complicated by
table 2
№ payment order |
Learning tasks |
Teaching methods |
Initial acquaintance with a piece of music in the process of listening to music, singing, music and rhythmic movement |
Expressive performance by adults; explanation of the nature of the work, information about the music; conversation with children; the use of visual art tools |
|
Sequential learning of songs, round dances, dances, dances, exercises and mastering knowledge, skills, abilities |
Demonstration to adults of the techniques of performing songs, dances; explanations and instructions for children during their performance — exercises for children in mastering skills (individual, group) |
|
Consolidation of knowledge and skills; practicing the expressiveness of singing, dancing, playing games |
Repeated repetitions of individual "difficult" places and the whole work; evaluation of the expressiveness of children's performance by adults and the children themselves; final conversation and evaluation of the performance of the learned work |
|
Checking the learned repertoire and the quality of mastering knowledge, skills and abilities |
Systematic observation of each participant in the process of collective action; individual survey in the course of learning; random testing of acquired knowledge and skills for a specific study period (month, quarter); execution of learned works on holidays, entertainment, monitoring the independent activities of children in order to identify their interests and the correctness of the ways of creative actions they acquired |
that each song, game, dance is at a different stage of their assimilation by children. Consequently, in the classroom it is necessary to keep track of many moments at the same time, especially how the tasks of education and development are solved in the process of learning.
Despite the conditional separation of the tasks of learning and development, one can draw up another exemplary scheme that makes it easy to trace the tasks of developing musical abilities and teaching methods that contribute to overall musical development (see Table 3, p.35).
Thus, teaching methods develop musical abilities, awaken the desire for independent creativity in any type of musical activity.
Table 3
No. p / p |
Tasks for the development of musical abilities |
Teaching methods |
The development of an emotional response to music |
Expressive performance of works of various genres and subjects; comparison of musical works with works of literature and visual arts; figurative characteristics of musical works |
|
The development of musical and sensory abilities |
Explanation and illustration of the sensory properties of music (pitch, rhythmic, timbre and dynamic), their graphic representation; exercises in distinguishing these properties; application of information in the process of practical exercises; independent use of musical and didactic games with sensory tasks |
|
The development of the harmony-melodic hearing, feelings of melodic intonations |
Exercises in the definition of two different musical heights, melody movements (up and down); acquaintance with the graphic image of the melodic line; systematic performance of singing exercises; singing unaccompanied after tuning in this key |
|
Development of a sense of rhythm |
Exercises performed by metrhythmic tasks in the process of movement (games, dances); exercises in defining various rhythmic patterns; familiarization with the graphic image of the rhythm (quarters and eighths) |
|
The development of musical memory |
Exercises in sequential alternation of singing out loud and silently; exercises in determining the names of works by their fragments; exercises in the independent performance of the ear of the simplest melodies on children's musical instruments |
|
The development of musical creativity |
Exercises to acquire the skills of independent action in singing, playing on children's instruments of movement; exercises in self-inventing options for games, dance, dance; teaching children to search for actions in the development of sensory abilities; creative tasks as a method for the development of song, music and dance, creativity |
It should be noted that musical abilities are manifested in children unevenly. Their study allows the teacher to invent tasks of various difficulties.
Methods depend on many pedagogical conditions. Some of them at first glance contradict each other. For example, for musical development Repeating an assignment that is often based on a show is important. However, in children it is important to develop autonomy of action.
Relationships and contrasts are also traced in other methods:
the word of the educator (explanation, indication) and visual display of works of art, methods of their execution;
the word and actions of an educator aimed at developing a conscious attitude towards music, the ability to analyze and at the same time develop children’s desire for emotional experiences;
showing samples to be followed, and forming the ability to act independently;
exercises that reinforce acquired skills and developmental tendencies to independently solve creative problems.
Methodical techniques
Teaching methods are closely connected with methodical techniques. Reception- this is part of the method and performs a supporting role with it. There are many receptions, and each teacher chooses the most effective ones.
Receptions vary depending on whether whatteaches the teacher to sing, listen, play, dance, and whomteaches younger or older children. For example, performing the work “Clowns” by D. Kabalevsky for a hearing in older group, the teacher can first talk about funny clowns, all the time in motion. But, playing the Russian folk tune “Do not be late” to the same children for the subsequent game, the teacher invites them to find out when to change the nature of the movement. Appearing in the second
parts accents tell children when to clap. Thus, the guys distinguish changes in the character of the music and independently determine the movements corresponding to them. They are ready to play.
Learning techniques vary with the age of the children. Take for example the learning of a song. Babies need to be interested in understandable to them, specific images. Before performing the song “Bird” by M. Rauhverger, the teacher shows a toy bird and says: “A bird flew in, sat on the window and tweeted. Children began to ask - wait, do not fly away! And the bird flew away (hiding the bird) - ah! Kids, do you want a bird to fly in? I'll call her and sing a song. ” The teacher puts the toy on the piano and sings. Thus, this methodical method acquires a playful character, the image of a bird becomes accessible, vivid and complements the expressive performance of the song.
In older groups there is no need to use this technique. The introductory word will help create a mood related to the character of the song being played. If the teacher wants to strengthen the artistic impression, then it is good to read a poetic passage, to show an illustration. So, when reading the song “This is our Homeland” E. Tilicheeva, the teacher reads the verses by S. Mikhalkov:
The Kremlin stars above us burn
Everywhere their light comes,
Good Motherland has guys
And there is no better country than that.
A variety of techniques are designed to bring up children’s conscious attitude to the learning process and at the same time encourage an emotional response to everything that happens. For example, in the song “Marsh” by M. Krasev, it is necessary to achieve the exact fulfillment of the rhythmic pattern in the phrase:
In order for the children to understand the task, the teacher says: “Let's sing the word“ sing out ”and hear how the sounds of the drum are heard.” Thus, children not only perform the melody rhythmically correctly, but also perceive the expressive meaning of the rhythm. At the same time, they emotionally respond to the invocatory sound of this part of the melody.
In preschool didactics emphasizes the importance of teaching methods that contribute to the development of independent activities. These techniques are also used in listening to music, when the teacher encourages children to make statements about music, to correct, interesting remarks The independence of children can also manifest itself in the performance of tasks, in search of ways to solve them. It is advisable techniques aimed at the development of auditory self-control, to assess the quality of performance in other children.
Independent actions of children do not exclude the demonstration of performance techniques. Even when teaching adults music, along with explanations, sometimes showing individual techniques is used. Moreover, it is necessary in the process of teaching preschoolers to compare the sound of a singing or moving song, to help correctly reproduce a difficult melody, to show individual movements in the dance, a characteristic feature of a music-playing image.
Training methods and teaching methods are closely linked. The methods indicate the ways in which the teacher conveys, and the child learns the musical material, the necessary performing skills, and the ability to act independently. Methodical techniques complement and specify methods. Using them, the teacher has the opportunity to show their pedagogical skills, fiction and creative initiative.
QUESTIONS AND TASKS
1. List the methods of musical education.
2. Explain why expressive music can be considered as a method of musical education for children.
3. Expand the nature of conversations about music, the need for their imagery, brevity, expressiveness and accuracy.
4. Compare the value of the teacher showing the techniques of singing, movement and independent actions of children.
5. What is the developmental nature of learning in music classes?
6. Formulate teaching methods depending on specific educational tasks, on the tasks of developing musical abilities.
7. Write the approximate content of the conversation with children 6-7 years old about a new work for them.
8. Create for yourself a certain educational task when learning a song, playing and think over methodical techniques.
9. Develop methodological techniques for the development of song, music and gaming creativity.
10. Make a summary of the consistent learning of the game, the round dance in the junior and preparatory groups and set what is their difference.
LITERATURE
Lenin V.I.About literature and art. - M., 1969.
Materials XXVII Congress of the CPSU.- M., 1986. Constitution (Basic Law) of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics.-M., 1978.
*
Vetlugina N.A. Musical education and all-round development of the child in the Soviet kindergarten// Musical education in the modern world. - M., 1973.
Vetlugina N.A. Musical education in kindergarten. - M., 1981.
Education and training in kindergarten / Ed. A.V. Zaporozhets, TA Markova. - M., 1976.
Kabalevsky, D. B. About three whales and about much more. - M., 1972.
Kabalevsky, D. B. The ideological foundations of musical education in the Soviet Union // Musical education in the modern world. - M., 1973.
Shatskaya V.N. Musical and aesthetic education of children and youth. - M., 1975.
Aesthetic education in kindergarten / Ed. ON. Vetlugina - M., 1985.
... Each of the activities
peculiar, possesses
their special qualities and
therefore renders its nothing
non-replaceable influence
A.P. Usova
Methods of musical education in kindergarten: “Doshk. education "/ N.A. Vetlugina, I.L. Dzerzhinskaya, L.N. Komissarova et al .; Ed. ON. Vetlugina - 3rd ed., Corr. and add. - M .: Education, 1989. - 270 pp .: notes.
Before we talk about the methodological techniques, you need to know what is meant by this "phrase". V.Ya. Kikotya, A.M. Stolyarenko gives the following definition: Methodical techniques are psychologically legitimate and pedagogically oriented methods of short-term actions of a teacher and the actions of students that are adequate to them, ensuring the achievement of the objectives of the lesson.
At the same time, they say that a set of methodological techniques “gives rise to” the method, and the complex use of the methods “gives life” to organizational forms.
Morozova S.A. It offers a fairly simple definition of methodical reception - these are actions aimed at solving a specific problem.
A common definition is given by E.A. Pevtsova: a methodical technique is a private means by which, in conjunction with other means, one or another way of knowing legal reality and acquiring skills in the field of law is realized.
Thus, the use of various teaching methods improves certain actions that are aimed at solving the set tasks. They constitute the concept of "methodological techniques." Didact M.I. Makhmutov calls them "an integral part of the method", with which all the authors of the above definitions agree in principle: V.Ya. Kikotya, A.M. Stolyarenko called the set of methodological techniques method; Morozova S.A. uses the phrase "an integral part of the method" in his work, and EA Pevtsova calls methodical technique a private remedy.
Methodical techniques are a set of teaching methods, i.e. methods of activity of the teacher and methods of activity of pupils adequate to them. Methodical techniques are actions aimed at solving a specific problem. These are work methods that are performed to achieve specific results and which can be expressed in the form of a list of actions. The methods of work (teaching) of students depend on the methods of activity of the teacher.
Moreover, for the effective use of techniques it is necessary to apply them in conjunction with pedagogical means - this is the tool with which the teacher solves the tasks facing him. With the help of learning tools it is possible to accelerate the process of mastering educational material (Appendix 1).
The same system of teaching methods of organization learning activities is a component of a study session on the law. At the same time, they pay attention to the rationality and efficiency of time use in the lessons of law. Experts believe that the assimilation of legal information is carried out unequally at different stages of the lesson. So, from the first to the fourth minute, students are able to learn only 60% of the material, and from the fourth to the twenty-third - 90%, and from the twenty-third to the thirty-fourth, 50% of the information that is offered in the lesson. From the thirty-fourth to the forty-fifth minute, the percentage of information learning falls. Considering these features, the law teacher builds his own system of organizing educational activities in the classroom, realizing that at the end of the lesson a new material should not be given, ending with clear final conclusions (for example, a psychological technique is used explaining that the “ending remains for a long time in a person’s memory” ).
Students should be distracted from the monotonous tiresome activities, often varying methods of teaching.
When choosing methodological techniques, it is necessary to consider:
1. How is the absorption of the material depending on the time of day. Experts state that the best period for the assimilation of complex legal material is determined by the time frame from 11 hours to 13 hours of the day. The rise in performance is observed on Saturday, since the students at the subconscious level have information about the approaching day off.
2. The presence and effectiveness of the use of visibility and technical means of teaching law.
3. The effectiveness of monitoring the work of students, the assessment of their activities.
4. The level of feedback shown during the lesson.
5. The degree of aesthetic impact classes for students.
Thus, the most common definition is given by E.A. Pevtsova: a methodical technique is a private means by which, in conjunction with other means, one or another way of knowing legal reality and acquiring skills in the field of law is realized. Methodical technique can also be defined as an integral part of the method.
For the effective use of techniques it is necessary to apply them in conjunction with pedagogical means.
When choosing teaching methods, it is necessary to take into account a number of requirements (the effectiveness of monitoring the work of students, the level of feedback shown during the lesson, how material is learned depending on the time of day, etc.), and students should also be distracted from monotonous tedious activity , often varying the methodical methods of legal education.
Subtleties of pedagogy:
Stages of education at different stages of development of society
The stage of the primitive communal stage of development According to the official (secular) science, humanity begins its history in primitive communal relations. It is a relationship between members of a population of creatures, based on a temporary (2) - of necessity, in connection with an important event, such as hunting or ...
Complex objectives of modern foreign language teaching
The starting point in determining the strategic goal of education is the social order of society in relation to the younger generation. In particular, foreign language education for almost the entire twentieth century consisted in the qualitative ownership of the subject. Then there was a turn from grammar ...
The content, forms and methods of teaching students in grades VII-VIII when mastering technological operations on a screw-cutting lathe
In the first chapter of qualification work, we uncovered the theoretical foundations of teaching students in grades VII-VIII when mastering technological operations on screw-cutting machines, identified the initial prerequisites for developing the necessary knowledge and skills of students in program content ...
- Riddles for girls on 8
- When on the ship two flags
- Order on the creation of the duty dispatch service
- Historical flags of the states of 1700
- The role-playing game as the main type of games for preschoolers place in the structure of children's games
- Logic Tricks for Adults
- Medical Institute with budget places

 Live journal
Live journal Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter